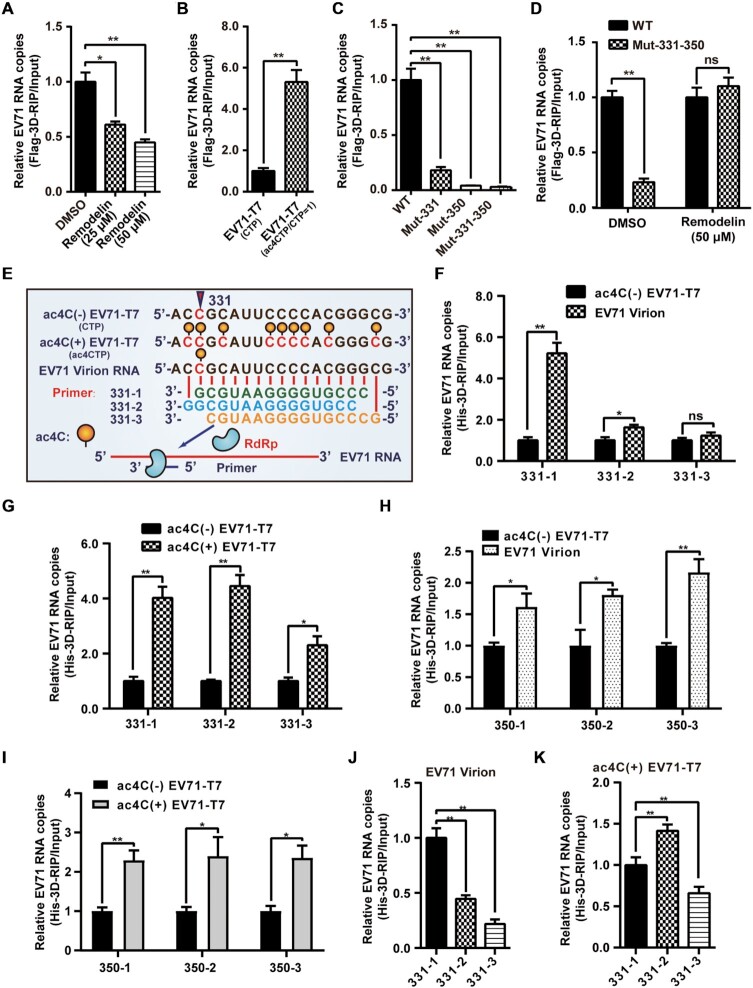
Figure 5.
ac4C promoted the binding of EV71 RNA to 3D. (A, D) Binding of 3D to EV71 RNA following NAT10 inhibition using remodelin. Vero cells overexpressing Flag-3D were treated with DMSO or remodelin and infected with EV71 (A) or EV71 WT and ac4C mutants (D). Crosslinking with formaldehyde and IP using anti-Flag antibodies were performed, followed by quantification using qPCR. Data are means ± SEMs (n = 3). *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ns: not significant, unpaired Student's t-test. (B, C) Binding of 3D to EV71 RNA with different ac4C modification levels. Vero cells with Flag-3D overexpression were transfected with EV71 genomes with (ac4CTP/CTP = 1) or without (CTP) ac4C (B) or infected with EV71 WT and ac4C mutants (C). The same treatment as used in (A) and (D). Data are means ± SEMs (n = 3). *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, unpaired Student's t-test. (E) Schematic of in vitro RNA binding assays near position 331. Yellow solid circles indicate the ac4C modification. (F–K) Binding of 3D and 331 or 350 primer-EV71 RNA pairs in vitro. EV71 RNAs extracted from T7 transcripts (ac4C[±]) or virions were annealed with 331- or 350–1/2/3 primers. His-3D was added, and samples were subjected to IP with anti-His antibodies, followed by quantification using qRT-PCR. Data are means ± SEMs (n = 3). *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ns: not significant, unpaired Student's t-tests. Data represent the comparison of 3D binding levels between ac4C(-) EV71-T7 and virion RNA (F & H) or ac4C(+) EV71-T7 (G & I). Alternatively, data show the binding levels of different 331 primers annealed with virion RNA (J) and ac4C(+) EV71-T7 (K).