Figure 3.
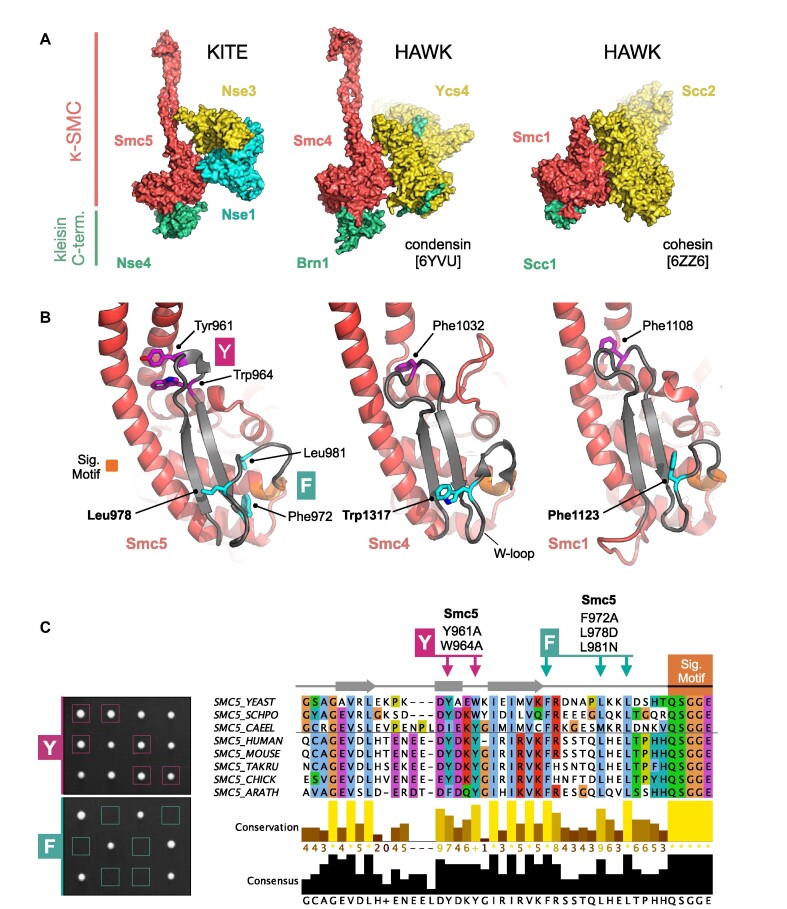
KITES and HAWKS share a common interaction interface involving the κ-SMC ‘W-loop’. (A) Side-by-side visualisation of the κ-SMC head domain from Smc5/6 (left), condensin (middle) and cohesin (right) in complex with their respective kleisin C-terminal domain; Nse4, Brn1 and Scc1. In each case, the interacting partner, whether KITE or HAWK, makes a similar set of interactions with the head domain of the κ-SMC. (B) Expanded view, showing secondary structure molecular cartoons for each κ-SMC head domain, highlighting the position of conserved amino acids within the ‘W-loop’ or equivalent (stick representation, carbon atoms coloured cyan) plus aromatic residues within the preceding sequence (stick representation, carbon atoms coloured magenta). The ABC-signature motif is additionally highlighted in orange. (C, left) Tetrad dissections. Spores derived from diploid S. cerevisiae strains carrying both wild-type allele and indicated mutant allele plus associated NAT-selectable marker (natMX6). Genotypes were confirmed by replica plating of spores on selective media (not shown). (C, right) Multiple sequence alignment, across selected species, showing conservation and consensus of amino acids within the W-loop and preceding region of Smc5 (produced using Jalview 2 with Clustal X colour scheme; (73)). Sets of compound mutations introduced into budding yeast: Smc5-Y = Y961A, W964A; Smc5-F = F972A, L978D, L981N. Please also see associated key for additional detail.