Fig. 3. Temperature-dependent optical waveguiding.
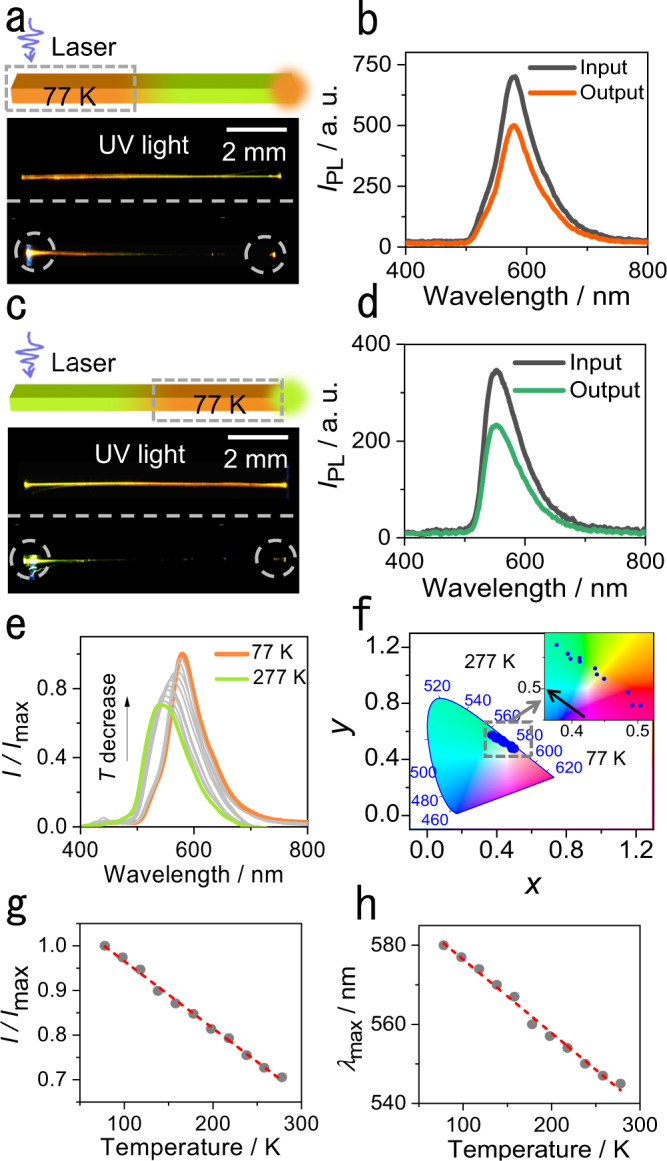
a Schematic diagram and real picture of a crystal waveguide at low temperature. The gray dashed box denotes the area where the liquid nitrogen was dropped (77 K). b Emission spectra recorded at the excitation end (77 K) and at the output end of the crystal (230 K). c Schematic diagram and real picture of a crystal waveguide at room temperature. d Emission spectra recorded at the excitation end (230 K) and at the output end of the crystal (77 K). e Emission spectra of the crystal optical waveguide at different temperatures. f CIE 1931 color space coordinates of crystal optical waveguide signals at different temperatures. The region in the boxed area is shown as zoomed-in image in the inset. g Correlation between the emission intensity ratio and temperature in the temperature range 77–277 K. The straight broken line shows a linear fit to the data. h Correlation between the crystal waveguide emission wavelength and temperature in the temperature range 77–277 K. The straight broken line shows a linear fit to the data.
