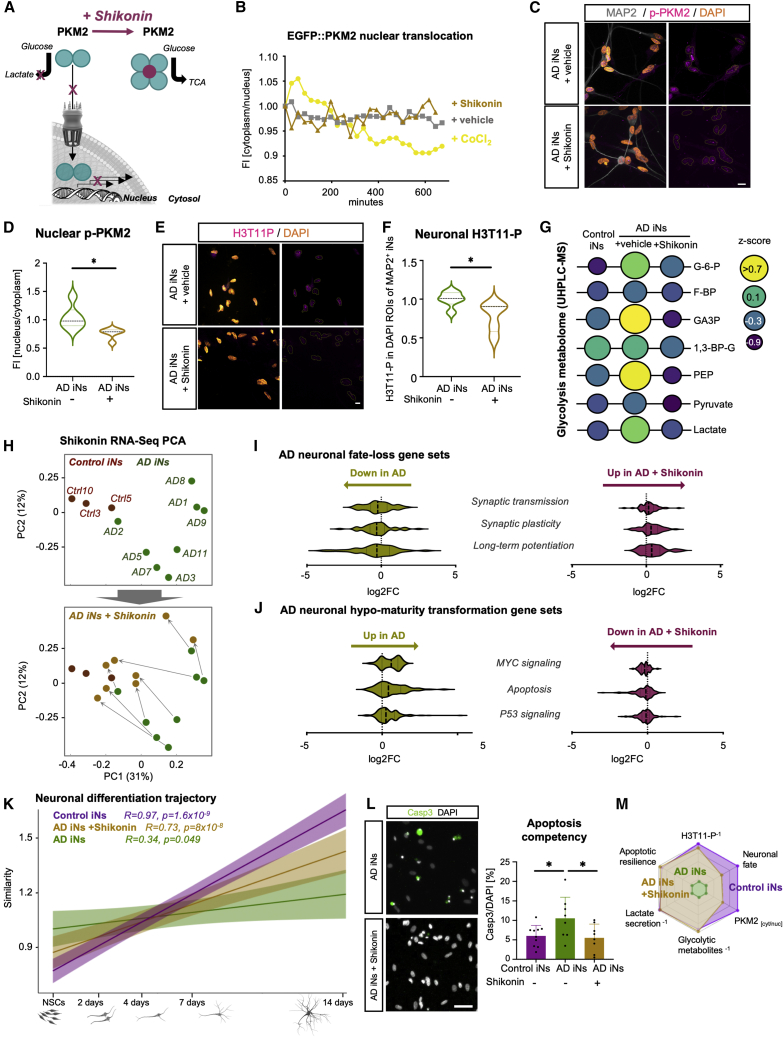
Figure 7.
PKM2 inhibition ameliorates PKM2-induced apoptotic competency
(A) Schematic: shikonin treatment prevents PKM2 nuclear translocation and increases metabolic enzymatic activity.
(B) Longitudinal EGFP::PKM2 localization in vehicle-treated (n = 3), CoCl2-treated (n = 4), and CoCl2+shikonin-treated (n = 4) control iNs.
(C–F) Immunostaining and quantification of nuclear p-PKM2 (C and D) and H3T11-P (E and F) in AD iNs with and without shikonin (vehicle, n = 6; shikonin, n = 5). Scale bars, 10 μm.
(G) Glycolytic metabolites measured by UHPLC-MS-based metabolomics. Size and color of the circles are indicative of abundance (control, n = 3; AD, n = 4; AD-shikonin, n = 4).
(H) PCA-based bulk RNA-seq (control, n = 3; AD and AD-S, n = 8).
(I and J) Transcriptomic analysis of AD neuronal fate-loss gene sets (I) and hypo-maturity gene sets (J) in control (n = 3), AD (n = 8), and AD + shikonin iNs (n = 8) after 10 days of treatment.
(K) Similarity profiles of control, AD, AD + shikonin iNs to neuronal differentiation trajectory of neural stem cells to neurons (Schafer et al., 2019).
(L) Quantification of immunostainings for cleaved caspase-3/DAPI in control (n = 9), AD (n = 8), and shikonin-treated AD (n = 8) iNs (one-way ANOVA, DF: 25, F = 4.027, p = 0.03). Scale bars, 50 µm.
(M) Radar plot of described phenotype and rescue with shikonin.
(D–L) Dots represent individual donors throughout the figure. Bars, mean; error bars, SD; violin plots, median and quartiles. Significance: unpaired t test, ∗p < 0.05.