Figure 1:
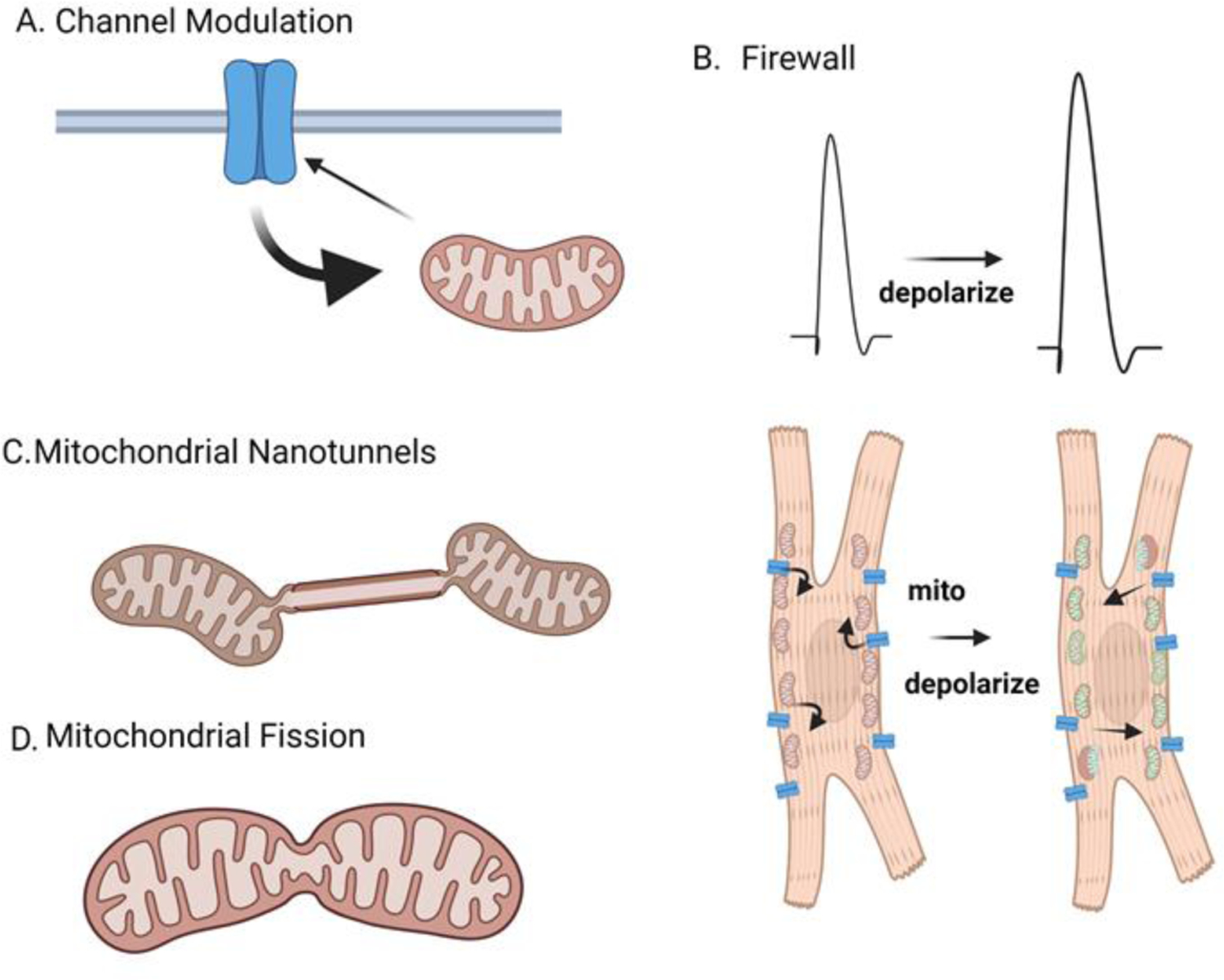
Mitochondria can influence Ca2+ transients of cardiomyocytes. The cartoon depicts different mechanisms by which mitochondria respond to altered cytosolic Ca2+levels. A) Mitochondria take up Ca2+ from store operated Ca2+ channels and prevent Ca2+ dependent inactivation of the channel. B) Mitochondria can serve as a firewall to prevent global increases in Ca2+. In atrial cardiomyocytes, Ca2+ entry across the sarcolemma (via cav1.2) is loaded into mitochondria that are present underneath the surface membrane. The amplitude of the Ca2+ transients becomes larger when cells are pretreated with agent that depolarize the mitochondrial membrane. C) Nanotunnels are specialized membrane extensions that connect two mitochondria. This phenomenon develops in cardiomyocytes with leaky Ca2+ release channels (RYR2). D) Elevated Ca2+ levels in the cytosol can trigger morphologic change to mitochondria called fission.
