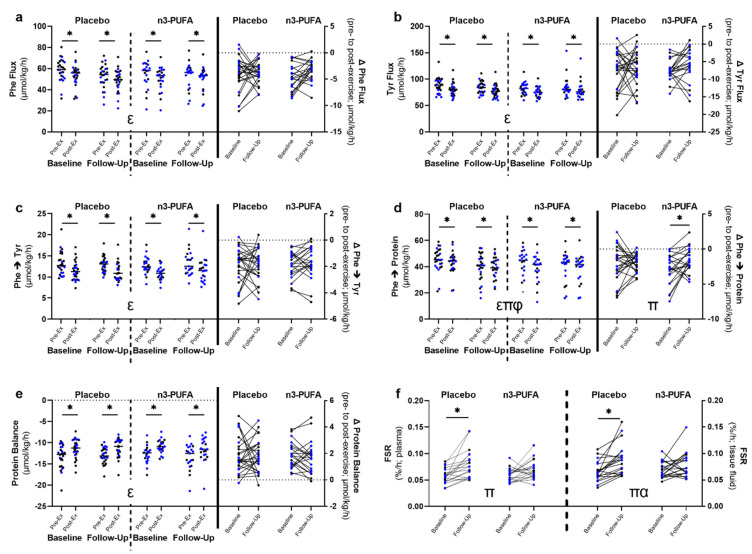
Figure 4.
The effects of 6-months of placebo or n3-PUFA on whole-body amino acid kinetic and skeletal muscle fractional synthesis rate responses to acute exercise. (a–e) Whole-body amino acid kinetics were measured pre- and post-acute exercise (pre-ex; post-ex, respectively) in older (65–85 years) adults before (baseline) and after (follow-up) 6-months of placebo or n3-PUFA supplementation administered in randomized, double-blind fashion. Kinetics were determined using the triple tracer approach and assessed (a) phenylalanine (Phe) flux; (b) tyrosine (Tyr) flux; (c) the conversion of phenylalanine to tyrosine (Phe→Tyr); (d) the conversion of phenylalanine to protein (Phe→protein); and (e) the balance between protein synthesis and protein breakdown (placebo: n = 26; n3-PUFA: n = 21). Steady state was achieved before and after an acute bout of resistance exercise, and the absolute change in kinetics from pre- to post-exercise (Δ) was calculated (a-e). (f) Mixed skeletal muscle protein fractional synthesis rates associated with acute exercise were measured before and after 6 months of placebo or n3-PUFA supplementation. Acute exercise-associated mixed muscle protein fractional synthesis rates were calculated from the isotopic enrichment of labeled amino acid tracers measured in serial muscle biopsies collected before and after acute exercise (placebo: n = 20; n3-PUFA: n = 20). Plasma and tissue fluid isotopic enrichments were used as precursor pools to determine the low and high limits of the true FSR. For the whole-body amino acid kinetics, mixed repeated measures ANOVAs were performed to determine the within-subjects effects of time (baseline, follow-up) and exercise (pre-ex, post-ex), the between-subjects effects of the intervention (n3-PUFA, placebo) and the interactions between time, exercise, and intervention. For the Δ and FSR values, mixed repeated measures ANOVAs were performed to determine the within-subjects effects of time (baseline, follow-up), the between-subjects effects of the intervention (n3-PUFA, placebo) and the interaction between time and intervention. Significance was set a priori at p < 0.05. Post hoc pairwise comparisons were performed when significant main or interaction effects were identified. Individual data points represent individual participants, with blue data points representing males and black data points representing females. Bars indicate mean and standard deviation. ε represents a significant main effect of exercise; π represents a significant main effect of time; φ represents a significant exercise-by-time interaction; α represents a significant time-by-intervention interaction; * represents a significant within-group difference based on post hoc pairwise comparisons. Phe: phenylalanine; Tyr: tyrosine; FSR: fractional synthesis rate.