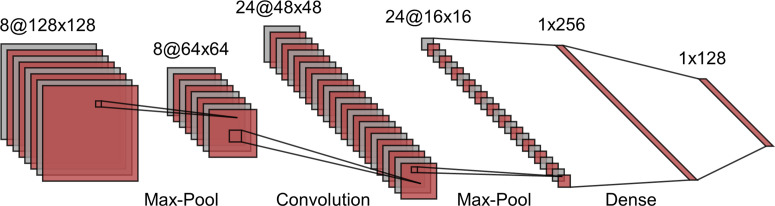
Figure 3.
An illustration of a simple convolutional neural network including convolutional, pooling, and fully connected layers. The two-dimensional input data undergoe multiple rounds of convolution and subsample layers. Feature extraction by filters are learned through back projection. The pooling operations, including max or mean, in a region are used to reduce the number of pixels in each layer of the network. Each operation increasingly extracts higher order discriminative features. Ultimately, the output layer is a class probability based on these higher order features.