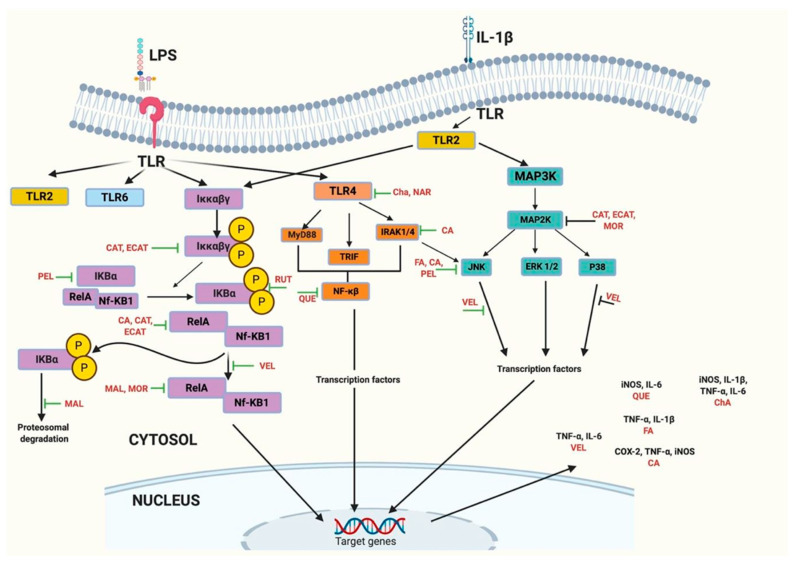
Figure 2.
Mechanism of action of some phenolic compounds found in lesser-consumed tropical fruits (lychee, mamey, passion fruit, açaí and jackfruit) and their ability to regulate the inflammatory process. Phenolic compounds can inhibit pro-inflammatory mediators such as IL-6, iNOS, IL-1β, TNF-α, COX-1, COX-2 by inhibiting their activity or gene expression. In addition, some phenolic compounds can up/downregulate transcriptional factors, such as nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) or Nrf-2, in inflammatory and antioxidant pathways. PEL: pelargonidine; CAT: catechin; ECAT: epicatechin; CA: caffeic acid; MOR: moracin; MAL: malvidin; VEL: velutin; RUT: rutin; QUE: quercetin; Cha: chlorogenic acid; NAR: naringenin; FA: ferulic acid.