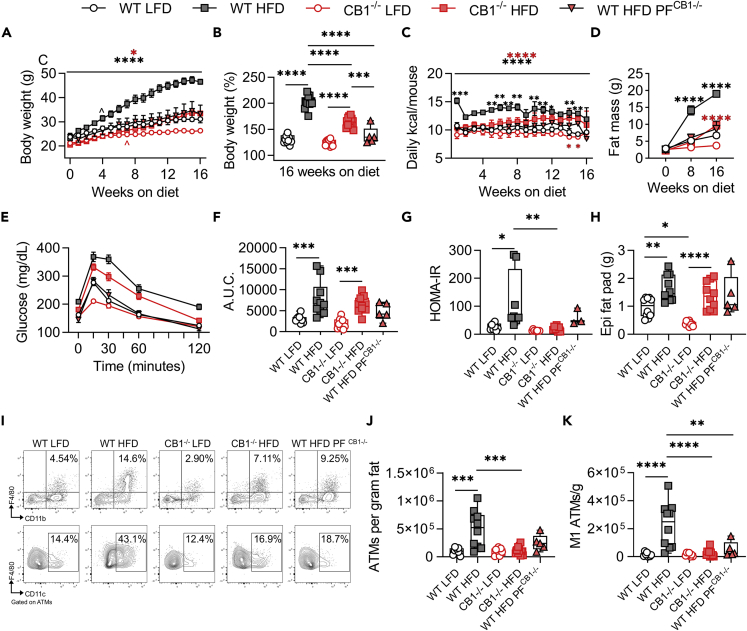
Figure 1.
Constitutive CB1 knockout reduces HFD-induced obesity and adipose tissue inflammation
6- to 8-week-old male mice were fed LFD or HFD for 16 weeks prior to metabolic and inflammatory evaluation.
(A) Body weight growth curves during 16 weeks of diet.
(B) Endpoint body weight expressed as percent of starting weight.
(C) Weekly means of daily calorie intake per mouse.
(D) DEXA fat mass at 0, 8, and 16 weeks on diet.
(E) Oral GTT performed during the 16th week of diet.
(F) GTT area under the curve (A.U.C.).
(G) HOMA-IR insulin resistance index after 16 weeks on diet.
(H) Epididymal fat pad wet weight.
(I) Representative flow cytometry contour plots of epididymal CD11b+F4/80+ ATMs and ATM-gated CD11c+ M1 ATMs.
(J) Quantification of ATMs per gram of epididymal fat.
(K) Quantification of M1 ATMs per gram of epididymal fat. Data are mean ± SEM or box and whisker plots with individual points representing biological replicates. N = 10 mice/group, except N = 5 for WT HFDPF CB1−/-. For C, N = 2 cages except N = 1 for WT HFDPF CB1−/-. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001 by one- or two-way ANOVA with Tukey post-hoc tests.