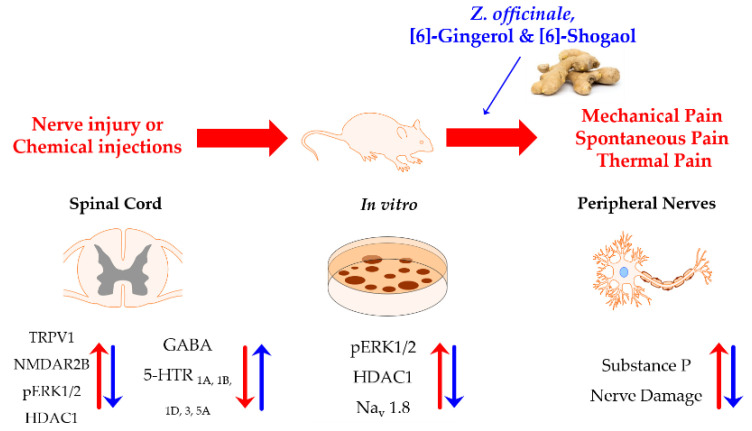
Figure 2.
The pathogenesis mechanism of pain induced by nerve injury or chemical injection and the mechanism of action of the analgesic effect of Z. officinale, [6]-gingerol and [6]-shogaol. Pain is caused by nerve injury or chemical injection (Red), and pain is attenuated when Z. officinale and its sub-components are administered (Blue). Mechanism was identified on the spinal cord, peripheral nerves and cultured cell (in vitro). Abbreviations:5-HTR (serotonin receptor), GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid), HDAC1 (histone deacetylase 1), Nav1.8 (voltage-gated sodium channel 1.8), NMDAR2B (N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunit 2B), pERK (phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated kinase), TRPV1 (transient receptor potential vanilloid 1), and Z. officinale (Zingiber officinale Roscoe).