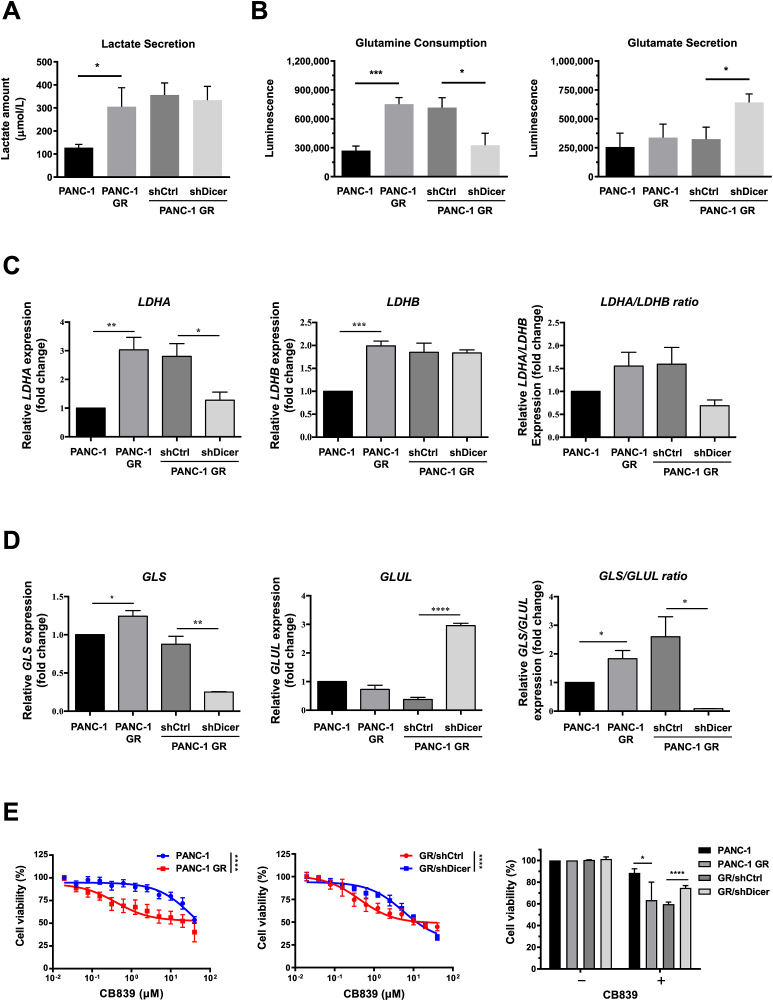
Figure 3.
Knockdown of Dicer in PANC-1 GR cells reduceglutamine metabolism. (A) Lactate secretion and (B) glutamine consumption (left panel) and glutamate secretion (right panel) of the indicated cells, namely PANC-1, PANC-1 GR cells, and PANC-1 GR cells with shDicer and shCtrl, were analyzed using the lactate colorimetric assay and glutamine/glutamate-Glo assay, respectively. Metabolic gene expression, including (C) the LDHA, LDHB, and LDHA:LDHB ratio and (D) GLS, GLUL, and GLS:GLUL ratio in PANC-1, PANC-1 GR, PANC-1 GR/shCtrl, and PANC-1 GR/shDicer cells were measured using qRT-PCR. The qRT-PCR data were normalized to the β-actin level in each individual sample, and a bar plot presents fold changes in the expression of PANC-1 cells. (E) The MTT assay was conducted to examine the viability of PANC-1 and PANC-1 GR cells (left panel), PANC-1 GR/shCtrl (GR/shCtrl) cells, and PANC-1 GR/shDicer (GR/shDicer) cells (middle panel) treated with various doses of the GLS inhibitor (CB839) for 72 h. Right panel, PANC-1, PANC-1 GR, GR/shCtrl, and GR/shDicer cells were incubated without (−, 0 μM) or with (+, 2.5 μM) CB839 for 72 h, and their viability was assessed using the MTT assay. The percentage of cell viability is relative to untreated controls. Results are presented as the means ± SEM of the three independent experiments. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, ∗∗∗P < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗P < 0.0001, two-tailed Student's t-test.