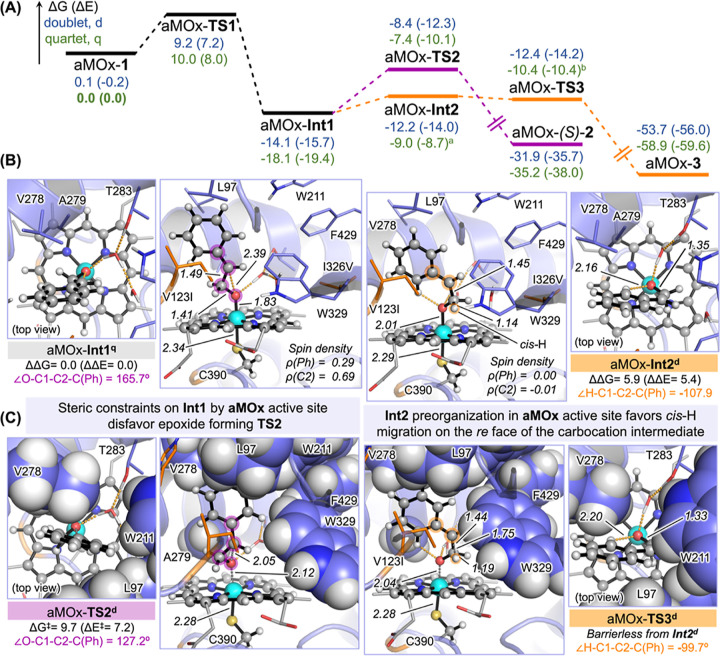
Figure 6.
QM/MM calculations on aMOx-catalyzed reaction pathways. (A) QM/MM-calculated reaction mechanism for the (S)-selective epoxidation and carbonyl formation pathways of styrene catalyzed by the aMOx variant (see also Figure S19). A representative snapshot from intermediate-bound MD simulations with styrene in the preferred reactive re face binding pose is used as the starting point (see Figure 4D). Relative Gibbs energies and electronic energies (ΔG and ΔE, respectively) are shown in blue for doublet (d) electronic state and green for quartet (q). Lowest-energy QM/MM-optimized structures for key (B) intermediates and (C) transition states are shown. Space-filling representations for key residues are used to highlight important steric constraints occurring in the active site. Energies, distances, angles, and spin density values are given in kcal·mol–1, angstroms (Å), degrees (°), and a.u., respectively. The QM/MM-calculated mechanism based on the minor explored si face NAC of styrene in the aMOx active site is reported in Figure S23. a Structure optimized with C2–cis-H, C2–trans-H, and cis-H–trans-H distances frozen. Distance values are taken from the optimized structure in the doublet state. Frequency calculations showed that the optimized structure has all positive frequencies. b The TS structure optimized with C2–cis-H, C1–cis-H, and O–C1 distances frozen. Distance values are taken from the optimized structure in the doublet state. Frequency calculations showed that all frequencies of the optimized structure are positive except one, which corresponds to the H-migration coordinate.