Fig. 5.
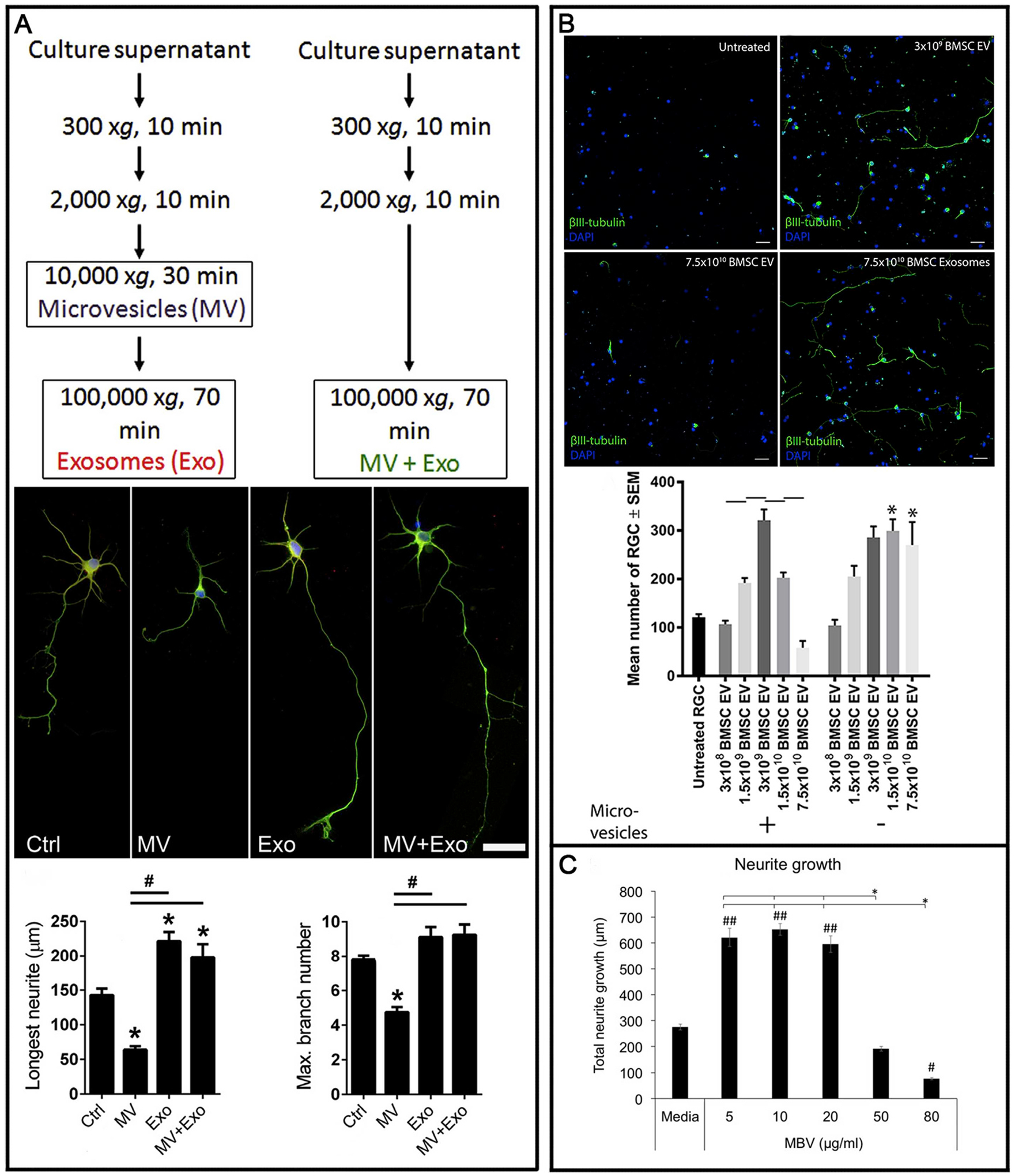
Differential effects of exosomes and microvesicles on retinal ganglion cells (RGC)/neurons. In three separate studies, one in cortical neurons (A) and 2 in RGC (B/C), exosomes demonstrated a neuritogenic/neuroprotective effect with microvesicles exerting the opposite. The first study (A) showed that exosomes were neuritogenic whereas the effect of microvesicles was worse than untreated controls. The second (B) demonstrated the efficacy of extracellular vesicles diminished at higher doses and this was due to the contamination of microvesicles. A third study (C) showed the same but did not confirm the effect was due to contaminating microvesicles. Modified Fig. 3 from Loppez-Verrilli et al. (2016) (A), Fig. 3 from Mead et al. (2017) (B), and Fig. 1 from van der Merwe et al. (2019), re-used under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CCBY4.0) licence.
