FIGURE 2.
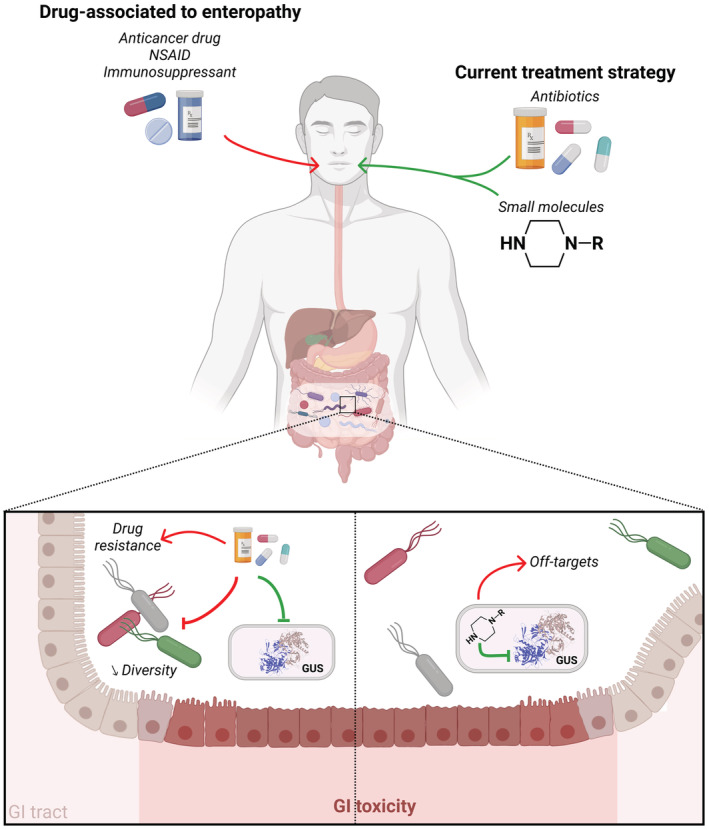
Current therapeutic strategies. Anticancer drugs, NSAID and immunosuppressants can cause GI toxicity and adverse effects through GUS activity. To counteract this toxicity, different approaches targeting this enzyme have been implemented. Antibiotics can eliminate GUS‐producing bacteria, but also commensal bacteria, favoring the selection of resistant strains and ultimately drug resistance. Some small molecules with a piperazine‐group can selectively inhibit GUS activity, but they may have off‐target effects and be involved in and drug–drug interactions. Illustration created with BioRender.com.
