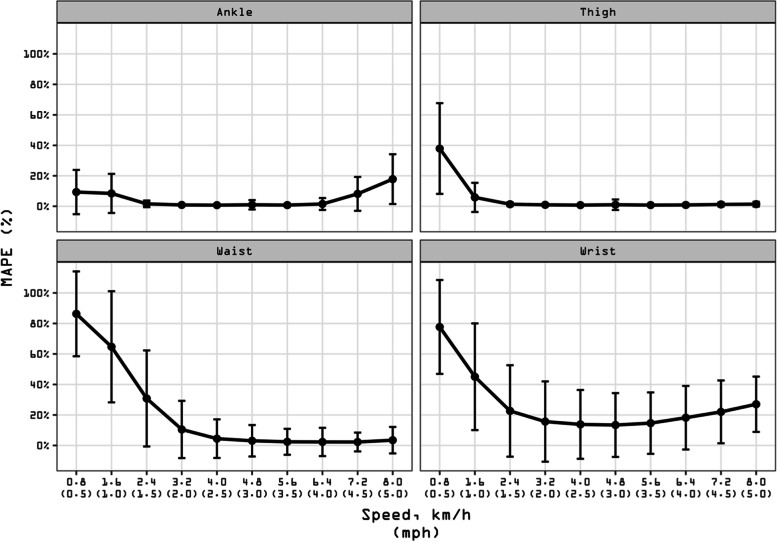
Fig. 2.
Mean absolute percentage error (MAPE) across walking speeds presented by wear location. Participants walked on a treadmill for 5-min bouts beginning at 0.8 km/h (0.5 mph) and increasing in 0.8 km/h (0.5 mph). MAPE (%) was computed for each person bout subtracting the directly observed steps (criterion measurement) from the wearable technology-derived steps and dividing it in absolute value by the directly observed steps. Black dots represent the averaged MAPE across specific wear location for a given speed. Bars represent standard deviation of MAPE. The standard deviation bars were not drawn when they were shorter than the height of the symbol. Lower MAPE values indicate higher wear location accuracy. Ankle-worn wearable: StepWatch (N = 253). Thigh-worn wearable: activPAL (N = 249). Waist-worn wearables: Actical (N = 250), ActiGraph GT9X (N = 254), Digi-Walker SW-200 (N = 258), Fitbit One (N = 160), Fitbit Zip (N = 98), GENEActiv (N = 224), NL-1000 (N = 258), PiezoRx (N = 98). Wrist-worn wearables: ActiGraph GT9X (N = 254), Apple Watch Series 1 (N = 174), Fitbit Ionic (N = 98), Garmin vivoactive 3 (N = 96), Garmin vivoactive HR (N = 77), Garmin vivofit 2 (N = 80), Garmin vivofit 3 (N = 77), GENEActiv (N = 217), Polar M600 (N = 97), Samsung Gear Fit2 (N = 80), Samsung Gear Fit2 Pro (N = 98). See Additional file 2 for a graphical classification of wearable technologies by age groups and Additional File 8: Suppl Table 1 for a tabular description of validity indices by wear locations