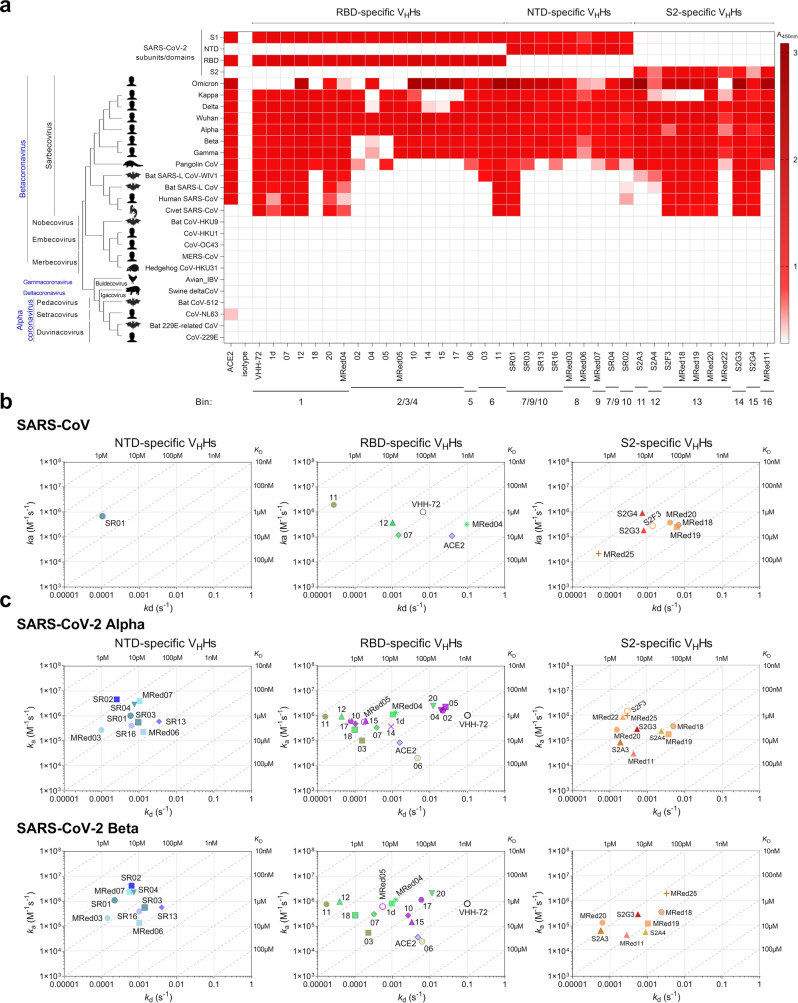
Fig. 2. Cross-reactivity of anti-SARS-CoV-2 S VHHs.
Data are organized based on VHH subunit/domain specificity and epitope bin designation (see Fig. 1d). a ELISA showing the cross-reactivity of VHHs against various coronavirus spike glycoprotein fragments, S, S1, S2, RBD and NTD. Shades of red represent binding, colorless boxes represent no binding. Assays were performed at a single VHH-Fc concentration. The “isotype” control (A20.1 VHH-Fc) shows no binding to S. Anti-SARS-CoV VHH-72 and ACE2-Fc were included as references. The phylogenetic tree of spike glycoproteins was constructed using MEGA1198. Source data used to generate the figure are included in Supplementary Data 1. b, c On-/off-rate maps summarizing VHH kinetic rate constants, kas and kds determined by SPR for the binding of VHHs to SARS-CoV S (b) and SARS-CoV-2 Alpha and Beta S (c). Diagonal lines represent equilibrium dissociation constants, KDs (see also Table 1). S2F3 cross-reacted to Alpha and Beta, as did S2G4 and MRed22 to Beta; however, poor fitting of SPR data precluded determining their kas, kds and KDs, hence their exclusion from relevant graphs. Maps were constructed using the VHH binding data from Supplementary Fig. 7 and Supplementary Table 4. Anti-SARS-CoV S VHH-72 and the monomeric ACE2 (ACE2-H6) are included as benchmark/reference binders.