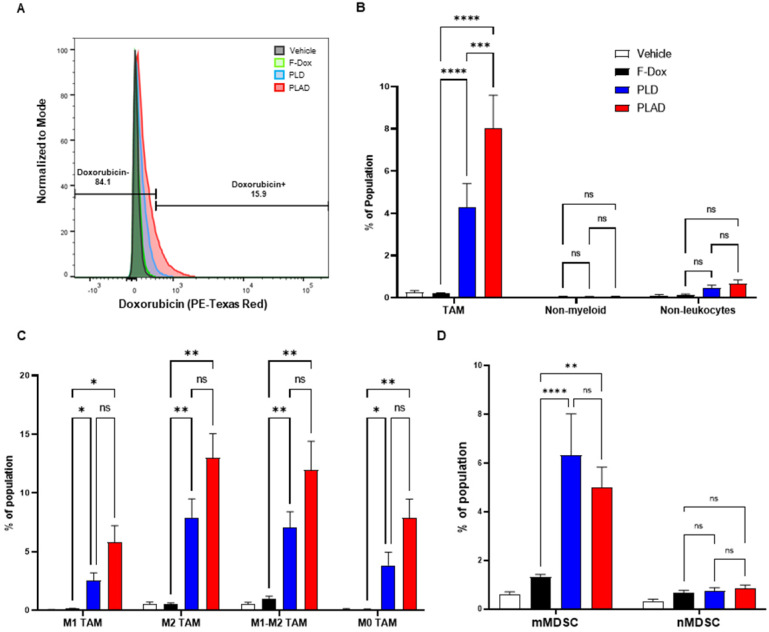
Figure 7.
Liposomal drug delivery significantly increases internalization of doxorubicin by TAM and mMDSC. (A) Gating strategy for doxorubicin fluorescence. (B) Doxorubicin uptake in TAM, non-myeloid leukocytes (i.e., lymphocytes), and non-leukocytes (i.e., tumor and stromal cells). (C) Doxorubicin uptake in TAM by polarization state and treatment. (D) Doxorubicin uptake in mMDSC and nMDSC. Data are mean with SEM, n=9 for PLAD, PLD and F-Dox, n=5 for vehicle; ANOVA with Tukey's test; *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, and ****p<0.0001. F-Dox: free doxorubicin, PLD: pegylated liposomal doxorubicin, PLAD: pegylated liposomal alendronate doxorubicin, TAM: tumor associated macrophages, mMDSC: monocytic myeloid derived suppressor cells, nMDSC: neutrophilic myeloid derived suppressor cells.