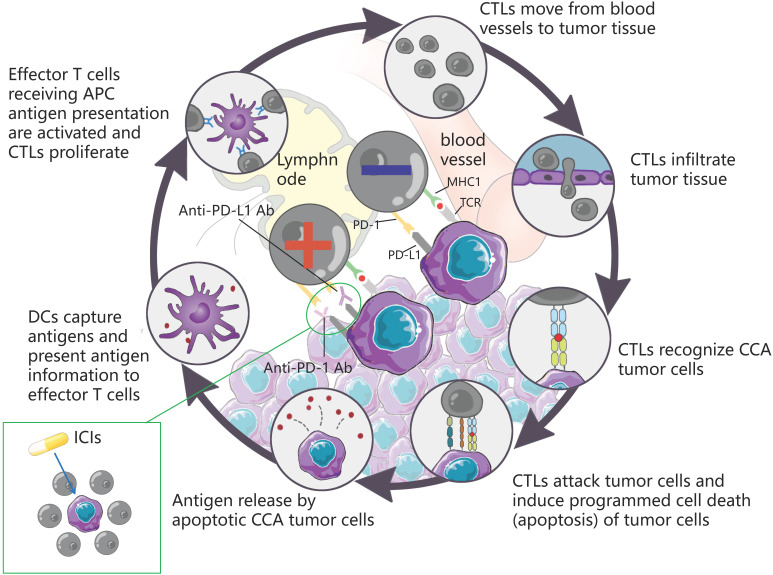
Figure 6.
DCs capture antigens, present antigen information to effector T cells, and effector T cells receiving APC antigen presentation are activated and CTLs proliferate. CTLs move from blood vessels to tumor tissue, recognize tumor cells and infiltrate tumor tissue, attack tumor cells, induce programmed cell death (apoptosis) of tumor cells, and subsequently apoptotic tumor cells release antigens to form a dynamic cycle. PD-1 is an important immunosuppressive molecule. It prevents the immune system from killing cancer cells by regulating the immune system's response to human cells downward, as well as regulating the immune system and promoting self-tolerance by suppressing T-cell inflammatory activity. PD-L1 is a ligand expressed on the surface of tumor cells. PD-L1 is up-regulated in a variety of tumor cells. It binds to PD-1 on CTLs and inhibits CTLs proliferation and activation, so that CTLs are in an inactivated state and finally induce immune escape. ICIs can block the binding of PD-1 and PD-L1, up-regulate the growth and proliferation of CTLs, enhance the recognition of CTLs to tumor cells, activate their attack and killing function, and achieve anti-tumor effect by mobilizing the body 's own immune function.