The molecules of the title compound are linked by weak N—H⋯N hydrogen bonds into [100] chains.
Keywords: aniline, crystal structure, N—H⋯N hydrogen bonds
Abstract
In the title compound, C7H7Br2N, the C—C—C bond angles of the benzene ring are notably distorted and two short intamolecular N—H⋯Br contacts occur. In the crystal, the molecules are linked by N—H⋯N hydrogen bonds to generate C(2) chains propagating in the [100] direction.
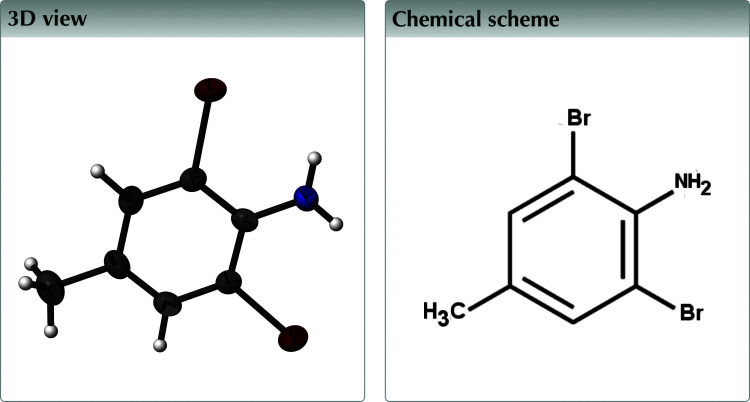
Structure description
The solid-state structure of the title compound, C7H7Br2N, was established by single-crystal X-ray diffraction analysis at 200 K and the molecular structure is illustrated in Fig. 1 ▸. The bromine atoms are slightly displaced from the mean plane of C1–C4/C6/C7 benzene ring, by 0.032 (1) and 0.065 (1) Å for Br1 and Br2, respectively. This can also be quantified by the C4—C3—C2—Br1 and C4—C6—C7—Br2 torsion angles, which are 179.7 (3) and −178.5 (3)°, respectively. The bond angles in the benzene ring are notably distorted from the ideal value of 120° with C7—C1—C2 = 115.1 (4), C1—C2—C3 = 122.8 (4) and C1—C7—C6 = 123.0 (4)°. The amine group lying between the bromine atoms results in two short intramolecular N—H⋯Br contacts (Table 1 ▸).
Figure 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound showing displacement ellipsoids at the 50% probability level.
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H1A⋯Br1 | 0.86 | 2.65 | 3.077 (4) | 112 |
| N1—H1B⋯Br2 | 0.86 | 2.64 | 3.072 (4) | 113 |
| N1—H1B⋯N1i | 0.86 | 2.38 | 3.120 (7) | 144 |
Symmetry code: (i)
 .
.
In the crystal, the molecules are linked by weak N1—H1B⋯N1 hydrogen bonds (Table 1 ▸) with N⋯N = 3.120 (7) Å to generate [100] C(2) chains with adjacent molecules related by the 21 screw axis. A similar hydrogen bond was observed in diaminomesithylene (Brihi et al., 2016 ▸). The packing is illustrated in Fig. 2 ▸, which shows the topology of the chain is a zigzag, with an angle of inclination of the benzene ring to the a axis of 53.73 (14)°.
Figure 2.
Views along the (a) b and (b) c axes of the crystal packing of the title compound with hydrogen bonds shown as dotted lines.
Synthesis and crystallization
The title compound is commercially available (Lancaster Synthesis). It was purified by recrystallization from a solution of 80% ethanol and 20% distilled water. The colorless single crystals obtained are in the form of needles, which grow along the a axis.
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details of the compound are summarized in Table 2 ▸.
Table 2. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | C7H7Br2N |
| M r | 264.96 |
| Crystal system, space group | Orthorhombic, P212121 |
| Temperature (K) | 200 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 4.3773 (7), 13.585 (2), 14.057 (3) |
| V (Å3) | 835.9 (2) |
| Z | 4 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 9.62 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.12 × 0.05 × 0.04 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Bruker APEXII QUAZAR CCD |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2016 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.396, 0.746 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 7550, 1715, 1422 |
| R int | 0.061 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.626 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.030, 0.072, 0.91 |
| No. of reflections | 1715 |
| No. of parameters | 92 |
| H-atom treatment | H-atom parameters not refined |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.36, −0.38 |
| Absolute structure | Flack (1983 ▸) |
| Absolute structure parameter | 0.02 (2) |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314622005776/hb4398sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314622005776/hb4398Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314622005776/hb4398Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 2175519
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Laboratoire de Cristallographie, Département de Physique, Université Mentouri-Constantine, Algérie and Institut Jean Lamour UMR 7198, Parc de Saurupt, CS 14234 F 54042 Nancy, France.
full crystallographic data
Crystal data
| C7H7Br2N | F(000) = 504 |
| Mr = 264.96 | Dx = 2.105 Mg m−3 |
| Orthorhombic, P212121 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: P 2ac 2ab | Cell parameters from 7750 reflections |
| a = 4.3773 (7) Å | θ = 2.1–26.4° |
| b = 13.585 (2) Å | µ = 9.62 mm−1 |
| c = 14.057 (3) Å | T = 200 K |
| V = 835.9 (2) Å3 | Needle, colorless |
| Z = 4 | 0.12 × 0.05 × 0.04 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker APEXII QUAZAR CCD diffractometer | 1715 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: ImuS | 1422 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.061 |
| Detector resolution: 8.02 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 26.4°, θmin = 2.1° |
| f\ and ω scans | h = −5→5 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2016) | k = −15→16 |
| Tmin = 0.396, Tmax = 0.746 | l = −17→17 |
| 7550 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.030 | H-atom parameters not refined |
| wR(F2) = 0.072 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0409P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 0.91 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 1715 reflections | Δρmax = 0.36 e Å−3 |
| 92 parameters | Δρmin = −0.38 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Absolute structure: Flack (1983) |
| 0 constraints | Absolute structure parameter: 0.02 (2) |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
Special details
| Geometry. Bond distances, angles etc. have been calculated using the rounded fractional coordinates. All su's are estimated from the variances of the (full) variance-covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account in the estimation of distances, angles and torsion angles |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > 2sigma(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Br1 | 0.69454 (12) | 0.51851 (3) | 0.40790 (4) | 0.0449 (2) | |
| Br2 | 0.49325 (11) | 0.11063 (3) | 0.35184 (3) | 0.0374 (2) | |
| N1 | 0.4343 (8) | 0.3124 (3) | 0.4488 (2) | 0.0340 (14) | |
| C1 | 0.6072 (9) | 0.3165 (3) | 0.3674 (3) | 0.0255 (14) | |
| C2 | 0.7481 (9) | 0.4015 (3) | 0.3360 (3) | 0.0277 (14) | |
| C3 | 0.9295 (10) | 0.4045 (3) | 0.2553 (3) | 0.0323 (17) | |
| C4 | 0.9781 (10) | 0.3217 (3) | 0.2004 (3) | 0.0313 (14) | |
| C5 | 1.1658 (11) | 0.3259 (3) | 0.1108 (3) | 0.0447 (17) | |
| C6 | 0.8409 (10) | 0.2336 (3) | 0.2315 (3) | 0.0317 (14) | |
| C7 | 0.6636 (10) | 0.2322 (3) | 0.3118 (3) | 0.0280 (12) | |
| H1 | 1.33755 | 0.28238 | 0.11654 | 0.0669* | |
| H1A | 0.40957 | 0.36443 | 0.48284 | 0.0407* | |
| H1B | 0.35064 | 0.25790 | 0.46576 | 0.0407* | |
| H2 | 1.02080 | 0.46361 | 0.23780 | 0.0388* | |
| H3 | 0.87095 | 0.17585 | 0.19722 | 0.0378* | |
| H4 | 1.23699 | 0.39194 | 0.10090 | 0.0669* | |
| H5 | 1.04240 | 0.30603 | 0.05765 | 0.0669* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Br1 | 0.0576 (3) | 0.0274 (2) | 0.0497 (3) | −0.0005 (2) | 0.0057 (3) | −0.0016 (2) |
| Br2 | 0.0373 (3) | 0.0279 (2) | 0.0471 (3) | −0.0053 (2) | −0.0027 (3) | 0.0002 (2) |
| N1 | 0.038 (3) | 0.031 (2) | 0.033 (2) | −0.0013 (18) | 0.0070 (18) | 0.0005 (17) |
| C1 | 0.0174 (19) | 0.028 (2) | 0.031 (3) | 0.0015 (17) | −0.0052 (19) | 0.007 (2) |
| C2 | 0.023 (2) | 0.027 (2) | 0.033 (3) | 0.0023 (18) | −0.0039 (19) | 0.0002 (19) |
| C3 | 0.027 (3) | 0.029 (3) | 0.041 (3) | 0.0011 (19) | 0.001 (2) | 0.006 (2) |
| C4 | 0.021 (2) | 0.041 (3) | 0.032 (2) | 0.005 (2) | 0.000 (2) | 0.007 (2) |
| C5 | 0.036 (3) | 0.057 (3) | 0.041 (3) | 0.009 (3) | 0.005 (3) | 0.008 (3) |
| C6 | 0.030 (2) | 0.038 (3) | 0.027 (2) | 0.004 (2) | −0.004 (2) | −0.002 (2) |
| C7 | 0.024 (2) | 0.028 (2) | 0.032 (2) | 0.001 (2) | −0.006 (2) | −0.0010 (19) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Br1—C2 | 1.898 (4) | C4—C5 | 1.505 (6) |
| Br2—C7 | 1.898 (4) | C4—C6 | 1.409 (6) |
| N1—C1 | 1.373 (5) | C6—C7 | 1.370 (6) |
| N1—H1A | 0.8600 | C3—H2 | 0.9300 |
| N1—H1B | 0.8600 | C5—H1 | 0.9600 |
| C1—C7 | 1.408 (6) | C5—H4 | 0.9600 |
| C1—C2 | 1.382 (6) | C5—H5 | 0.9600 |
| C2—C3 | 1.385 (6) | C6—H3 | 0.9300 |
| C3—C4 | 1.381 (6) | ||
| C1—N1—H1B | 120.00 | Br2—C7—C1 | 118.3 (3) |
| H1A—N1—H1B | 120.00 | Br2—C7—C6 | 118.6 (3) |
| C1—N1—H1A | 120.00 | C1—C7—C6 | 123.0 (4) |
| C2—C1—C7 | 115.1 (4) | C2—C3—H2 | 119.00 |
| N1—C1—C7 | 121.8 (4) | C4—C3—H2 | 119.00 |
| N1—C1—C2 | 123.1 (4) | C4—C5—H1 | 110.00 |
| Br1—C2—C1 | 118.3 (3) | C4—C5—H4 | 110.00 |
| Br1—C2—C3 | 118.8 (3) | C4—C5—H5 | 109.00 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 122.8 (4) | H1—C5—H4 | 109.00 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 121.5 (4) | H1—C5—H5 | 109.00 |
| C5—C4—C6 | 121.7 (4) | H4—C5—H5 | 109.00 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 121.4 (4) | C4—C6—H3 | 120.00 |
| C3—C4—C6 | 116.9 (4) | C7—C6—H3 | 120.00 |
| C4—C6—C7 | 120.6 (4) | ||
| N1—C1—C2—Br1 | −1.0 (5) | Br1—C2—C3—C4 | 179.7 (3) |
| N1—C1—C2—C3 | 178.1 (4) | C1—C2—C3—C4 | 0.6 (7) |
| C7—C1—C2—Br1 | −178.5 (3) | C2—C3—C4—C5 | 177.7 (4) |
| C7—C1—C2—C3 | 0.6 (6) | C2—C3—C4—C6 | −1.5 (6) |
| N1—C1—C7—Br2 | 0.1 (6) | C3—C4—C6—C7 | 1.2 (6) |
| N1—C1—C7—C6 | −178.5 (4) | C5—C4—C6—C7 | −178.1 (4) |
| C2—C1—C7—Br2 | 177.6 (3) | C4—C6—C7—Br2 | −178.5 (3) |
| C2—C1—C7—C6 | −1.0 (6) | C4—C6—C7—C1 | 0.1 (7) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H1A···Br1 | 0.86 | 2.65 | 3.077 (4) | 112 |
| N1—H1B···Br2 | 0.86 | 2.64 | 3.072 (4) | 113 |
| N1—H1B···N1i | 0.86 | 2.38 | 3.120 (7) | 144 |
Symmetry code: (i) x−1/2, −y+1/2, −z+1.
References
- Brihi, O., Hamdouni, N., Boulcina, R., Medjani, M., Meinnel, J. & Boudjada, A. (2016). IUCrData, 1, x160351.
- Bruker (2016). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Altomare, A., Cascarano, G., Giacovazzo, C., Guagliardi, A., Burla, M. C., Polidori, G. & Camalli, M. (1994). J. Appl. Cryst. 27, 435.
- Farrugia, L. J. (2012). J. Appl. Cryst. 45, 849–854.
- Flack, H. D. (1983). Acta Cryst. A39, 876–881.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314622005776/hb4398sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314622005776/hb4398Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314622005776/hb4398Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 2175519
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




