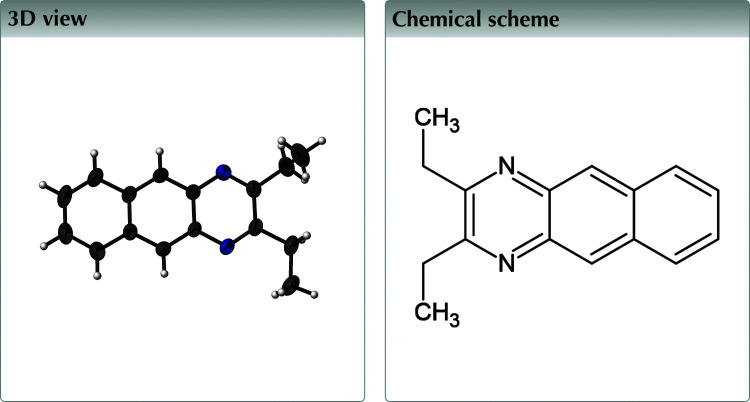
In the title compound, one of the pendant methyl groups lies close to the fused-ring plane and the other is significantly displaced.
Keywords: crystal structure, benzoquinoxaline
Abstract
The title compound, C16H16N2, was synthesized by dispersing 3,4-hexanedione in a methanol–water solution containing the acid catalyst NH4HF2, then adding 1,2-diaminonaphthalene. The fused-ring system of the title compound is close to planar (r.m.s. deviation = 0.028 Å); one of the pendant methyl C atoms lies close to the ring plane [deviation = 0.071 (2) Å; N—C—C—C = −0.27 (18)°] whereas the other is significantly displaced [–1.7136 (18) Å; 91.64 (16)°]. The molecules pack in space group I
 in a distinctive criss-cross motif supported by numerous aromatic π–π stacking interactions [shortest centroid–centroid separation = 3.5805 (6) Å].
in a distinctive criss-cross motif supported by numerous aromatic π–π stacking interactions [shortest centroid–centroid separation = 3.5805 (6) Å].
Structure description
The bond lengths and angles in the title compound fall within their expected values and the C3–C14/N1/N2 fused-ring system is close to planar (r.m.s. deviation = 0.028 Å). The C1 methyl atom lies close to the ring plane [deviation = 0.071 (2) Å; N1—C3—C2—C1 = −0.027 (16)°] whereas C16 is significantly displaced [deviation = −1.7136 (18) Å; N2—C14—C15—C16 = 91.64 (16)°] (Fig. 1 ▸).
Figure 1.
A view of the title compound with displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 50% probability level.
In the crystal, the molecles pack in a distinctive criss-cross motif (Fig. 2 ▸) in space group I
 with stacks of molecules propagating in the [001] direction. Numerous aromatic π–π stacking interactions help to consolidate the packing [shortest centroid–centroid separation = 3.5805 (6) Å].
with stacks of molecules propagating in the [001] direction. Numerous aromatic π–π stacking interactions help to consolidate the packing [shortest centroid–centroid separation = 3.5805 (6) Å].
Figure 2.
A view of the unit cell of the title compound along [001].
Synthesis and crystallization
2,3-Diethylbenzo[g]quinoxaline, C16H16N2, was prepared using the method used by Lassagne et al. (2015 ▸) to create 2,3-diarylpyridopyrazines. In a 50-ml Erlenmeyer flask equipped with a stir bar, 10.0 mmol of hexanedione (1.14 g) was dispersed in 20 ml of a 2.5 × 10−3 M NH4HF2 solution in MeOH and 2 ml of distilled water. To that stirred solution, 10.0 mmol of 1,2-naphthalenediamine (1.58 g) was added. The solution was allowed to stir overnight despite evidence of product after the first hour: 1.44 grams of a pale whitish powder was filtered and washed with two 2 ml aliquots of ice-cold methanol (60.9% yield). The crude product was mostly pure by NMR but was further purified by recrystallization from a 50:50 methanol/toluene solution (1.11 g recovered, 47.0% yield overall). (m.p. 411 K) ATR–IR (cm−1) 2981, 2934, 1703, 1575, 1455, 1351, 1325, 910, 889, 754; 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.58 (s, 1H), 8.07 (m, 1H), 7.55 (m, 1H) 3.09 (q, 2H), 1.49 (t, 3H); 13C (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ 158.14, 138.06, 133.24, 128.35, 126.57, 126.15, 28.63, 12.07. Crystals for the diffraction experiment were grown from slow evaporation of a methylene chloride solution. FTIR, 1H NMR, and 13C NMR spectra are given as supporting information.
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 1 ▸. The absolute structure of the crystal chosen for data collection was indeterminate in the refinement reported here.
Table 1. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | C16H16N2 |
| M r | 236.31 |
| Crystal system, space group | Tetragonal, I

|
| Temperature (K) | 293 |
| a, c (Å) | 13.93535 (18), 13.1629 (3) |
| V (Å3) | 2556.16 (7) |
| Z | 8 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.07 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.39 × 0.33 × 0.27 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Rigaku Xcalibur, Sapphire3 |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Rigaku, 2018 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.922, 1.000 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 31103, 4779, 3869 |
| R int | 0.031 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.778 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.048, 0.136, 1.04 |
| No. of reflections | 4779 |
| No. of parameters | 165 |
| H-atom treatment | H-atom parameters constrained |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.28, −0.14 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S241431462000454X/hb4346sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S241431462000454X/hb4346Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S241431462000454X/hb4346Isup4.cml
Supplementary Material (FTIR, 1H NMR, 13C NMR). DOI: 10.1107/S241431462000454X/hb4346sup3.pdf
CCDC reference: 1994287
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by a CCSU–AAUP research grant.
full crystallographic data
Crystal data
| C16H16N2 | Melting point: 411 K |
| Mr = 236.31 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Tetragonal, I4 | Cell parameters from 7488 reflections |
| a = 13.93535 (18) Å | θ = 4.6–31.8° |
| c = 13.1629 (3) Å | µ = 0.07 mm−1 |
| V = 2556.16 (7) Å3 | T = 293 K |
| Z = 8 | Block, white |
| F(000) = 1008 | 0.39 × 0.33 × 0.27 mm |
| Dx = 1.228 Mg m−3 |
Data collection
| Rigaku Xcalibur, Sapphire3 diffractometer | 4779 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed X-ray tube, Enhance (Mo) X-ray Source | 3869 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.031 |
| Detector resolution: 16.1790 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 33.6°, θmin = 4.3° |
| ω scans | h = −21→21 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlisPro; Rigaku, 2018) | k = −21→21 |
| Tmin = 0.922, Tmax = 1.000 | l = −20→19 |
| 31103 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.048 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.136 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0756P)2 + 0.2732P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.04 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 4779 reflections | Δρmax = 0.28 e Å−3 |
| 165 parameters | Δρmin = −0.14 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Absolute structure: Flack H D (1983), Acta Cryst. A39, 876-881 |
| Primary atom site location: dual | Absolute structure parameter: 0 (2) |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > 2sigma(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. H atoms were included in calculated positions with C—H = 0.93–0.97 Å and refined as riding atoms with Uiso = 1.2Ueq(C) or 1.5Ueq(methyl C). Reflections affected by the beam stop were omitted from the refinement. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C1 | −0.29561 (13) | −1.16936 (12) | −0.44274 (13) | 0.0600 (4) | |
| H1A | −0.3206 | −1.1110 | −0.4711 | 0.090* | |
| H1B | −0.3333 | −1.2227 | −0.4659 | 0.090* | |
| H1C | −0.2302 | −1.1776 | −0.4640 | 0.090* | |
| C2 | −0.29974 (10) | −1.16422 (10) | −0.32887 (12) | 0.0493 (3) | |
| H2A | −0.2793 | −1.2256 | −0.3016 | 0.059* | |
| H2B | −0.3660 | −1.1546 | −0.3087 | 0.059* | |
| C3 | −0.23964 (8) | −1.08656 (8) | −0.28133 (10) | 0.0379 (2) | |
| C4 | −0.13277 (8) | −0.96118 (8) | −0.29463 (9) | 0.0328 (2) | |
| C5 | −0.07941 (9) | −0.89899 (9) | −0.35476 (9) | 0.0378 (2) | |
| H5 | −0.0815 | −0.9047 | −0.4251 | 0.045* | |
| C6 | −0.02254 (8) | −0.82781 (8) | −0.31001 (9) | 0.0360 (2) | |
| C7 | 0.03189 (10) | −0.76181 (10) | −0.36928 (12) | 0.0475 (3) | |
| H7 | 0.0310 | −0.7661 | −0.4398 | 0.057* | |
| C8 | 0.08527 (12) | −0.69247 (11) | −0.32317 (15) | 0.0567 (4) | |
| H8 | 0.1199 | −0.6493 | −0.3627 | 0.068* | |
| C9 | 0.08872 (12) | −0.68520 (11) | −0.21668 (15) | 0.0608 (4) | |
| H9 | 0.1253 | −0.6372 | −0.1867 | 0.073* | |
| C10 | 0.03930 (10) | −0.74736 (11) | −0.15731 (12) | 0.0515 (3) | |
| H10 | 0.0430 | −0.7421 | −0.0870 | 0.062* | |
| C11 | −0.01854 (8) | −0.82097 (9) | −0.20173 (10) | 0.0369 (2) | |
| C12 | −0.07119 (8) | −0.88458 (9) | −0.14191 (9) | 0.0380 (2) | |
| H12 | −0.0676 | −0.8806 | −0.0715 | 0.046* | |
| C13 | −0.12889 (8) | −0.95376 (8) | −0.18678 (8) | 0.0333 (2) | |
| C14 | −0.23818 (8) | −1.07610 (9) | −0.17124 (10) | 0.0381 (2) | |
| C15 | −0.30438 (11) | −1.13340 (11) | −0.10459 (12) | 0.0522 (3) | |
| H15A | −0.2763 | −1.1398 | −0.0375 | 0.063* | |
| H15B | −0.3123 | −1.1972 | −0.1328 | 0.063* | |
| C16 | −0.40207 (12) | −1.08493 (14) | −0.09594 (16) | 0.0684 (5) | |
| H16A | −0.4299 | −1.0786 | −0.1623 | 0.103* | |
| H16B | −0.3945 | −1.0225 | −0.0661 | 0.103* | |
| H16C | −0.4434 | −1.1231 | −0.0539 | 0.103* | |
| N1 | −0.18907 (7) | −1.03067 (7) | −0.34033 (9) | 0.0388 (2) | |
| N2 | −0.18387 (7) | −1.01278 (8) | −0.12633 (8) | 0.0388 (2) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.0616 (8) | 0.0543 (8) | 0.0641 (10) | −0.0115 (7) | −0.0117 (8) | −0.0176 (7) |
| C2 | 0.0434 (6) | 0.0432 (7) | 0.0613 (9) | −0.0115 (5) | −0.0068 (6) | −0.0058 (6) |
| C3 | 0.0336 (5) | 0.0337 (5) | 0.0463 (6) | −0.0024 (4) | −0.0068 (5) | −0.0029 (4) |
| C4 | 0.0293 (5) | 0.0313 (5) | 0.0377 (5) | −0.0020 (4) | −0.0033 (4) | −0.0039 (4) |
| C5 | 0.0381 (5) | 0.0396 (6) | 0.0358 (5) | −0.0027 (4) | −0.0006 (4) | −0.0041 (4) |
| C6 | 0.0306 (5) | 0.0336 (5) | 0.0439 (6) | −0.0011 (4) | 0.0009 (4) | −0.0024 (4) |
| C7 | 0.0441 (6) | 0.0445 (6) | 0.0539 (8) | −0.0059 (5) | 0.0057 (6) | 0.0018 (6) |
| C8 | 0.0494 (8) | 0.0470 (7) | 0.0738 (11) | −0.0151 (6) | 0.0073 (7) | 0.0010 (7) |
| C9 | 0.0510 (8) | 0.0494 (8) | 0.0820 (12) | −0.0184 (6) | −0.0056 (8) | −0.0122 (8) |
| C10 | 0.0467 (7) | 0.0515 (7) | 0.0563 (8) | −0.0122 (6) | −0.0081 (6) | −0.0113 (6) |
| C11 | 0.0302 (5) | 0.0360 (5) | 0.0446 (6) | 0.0000 (4) | −0.0049 (4) | −0.0058 (4) |
| C12 | 0.0365 (6) | 0.0423 (6) | 0.0353 (5) | −0.0022 (4) | −0.0059 (4) | −0.0042 (4) |
| C13 | 0.0292 (5) | 0.0340 (5) | 0.0368 (5) | 0.0016 (4) | −0.0041 (4) | 0.0006 (4) |
| C14 | 0.0341 (5) | 0.0356 (5) | 0.0445 (6) | 0.0005 (4) | −0.0041 (5) | 0.0067 (5) |
| C15 | 0.0550 (8) | 0.0455 (7) | 0.0561 (8) | −0.0093 (6) | −0.0022 (6) | 0.0152 (6) |
| C16 | 0.0504 (8) | 0.0754 (11) | 0.0794 (11) | −0.0118 (8) | 0.0130 (8) | 0.0169 (9) |
| N1 | 0.0364 (5) | 0.0390 (5) | 0.0409 (5) | −0.0054 (4) | −0.0047 (4) | −0.0056 (4) |
| N2 | 0.0384 (5) | 0.0402 (5) | 0.0378 (5) | −0.0016 (4) | −0.0044 (4) | 0.0044 (4) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| C1—H1A | 0.9600 | C8—H8 | 0.9300 |
| C1—H1B | 0.9600 | C8—C9 | 1.406 (3) |
| C1—H1C | 0.9600 | C9—H9 | 0.9300 |
| C1—C2 | 1.502 (2) | C9—C10 | 1.355 (2) |
| C2—H2A | 0.9700 | C10—H10 | 0.9300 |
| C2—H2B | 0.9700 | C10—C11 | 1.4296 (16) |
| C2—C3 | 1.5047 (17) | C11—C12 | 1.3943 (17) |
| C3—C14 | 1.4566 (18) | C12—H12 | 0.9300 |
| C3—N1 | 1.3062 (16) | C12—C13 | 1.3873 (15) |
| C4—C5 | 1.3894 (15) | C13—N2 | 1.3772 (15) |
| C4—C13 | 1.4245 (15) | C14—C15 | 1.5027 (18) |
| C4—N1 | 1.3839 (13) | C14—N2 | 1.3042 (16) |
| C5—H5 | 0.9300 | C15—H15A | 0.9700 |
| C5—C6 | 1.3997 (16) | C15—H15B | 0.9700 |
| C6—C7 | 1.4247 (17) | C15—C16 | 1.524 (2) |
| C6—C11 | 1.4296 (17) | C16—H16A | 0.9600 |
| C7—H7 | 0.9300 | C16—H16B | 0.9600 |
| C7—C8 | 1.362 (2) | C16—H16C | 0.9600 |
| H1A—C1—H1B | 109.5 | C10—C9—C8 | 120.77 (14) |
| H1A—C1—H1C | 109.5 | C10—C9—H9 | 119.6 |
| H1B—C1—H1C | 109.5 | C9—C10—H10 | 119.7 |
| C2—C1—H1A | 109.5 | C9—C10—C11 | 120.63 (14) |
| C2—C1—H1B | 109.5 | C11—C10—H10 | 119.7 |
| C2—C1—H1C | 109.5 | C6—C11—C10 | 118.53 (12) |
| C1—C2—H2A | 108.4 | C12—C11—C6 | 120.01 (10) |
| C1—C2—H2B | 108.4 | C12—C11—C10 | 121.46 (12) |
| C1—C2—C3 | 115.34 (12) | C11—C12—H12 | 119.8 |
| H2A—C2—H2B | 107.5 | C13—C12—C11 | 120.42 (10) |
| C3—C2—H2A | 108.4 | C13—C12—H12 | 119.8 |
| C3—C2—H2B | 108.4 | C12—C13—C4 | 119.79 (10) |
| C14—C3—C2 | 119.57 (11) | N2—C13—C4 | 120.75 (10) |
| N1—C3—C2 | 118.81 (11) | N2—C13—C12 | 119.44 (10) |
| N1—C3—C14 | 121.62 (10) | C3—C14—C15 | 121.27 (11) |
| C5—C4—C13 | 120.14 (10) | N2—C14—C3 | 121.79 (11) |
| N1—C4—C5 | 119.49 (10) | N2—C14—C15 | 116.81 (12) |
| N1—C4—C13 | 120.37 (10) | C14—C15—H15A | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 119.8 | C14—C15—H15B | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 120.35 (10) | C14—C15—C16 | 110.89 (12) |
| C6—C5—H5 | 119.8 | H15A—C15—H15B | 108.1 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 121.91 (11) | C16—C15—H15A | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—C11 | 119.27 (11) | C16—C15—H15B | 109.5 |
| C7—C6—C11 | 118.82 (11) | C15—C16—H16A | 109.5 |
| C6—C7—H7 | 119.8 | C15—C16—H16B | 109.5 |
| C8—C7—C6 | 120.31 (13) | C15—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| C8—C7—H7 | 119.8 | H16A—C16—H16B | 109.5 |
| C7—C8—H8 | 119.5 | H16A—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| C7—C8—C9 | 120.93 (14) | H16B—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| C9—C8—H8 | 119.5 | C3—N1—C4 | 117.69 (10) |
| C8—C9—H9 | 119.6 | C14—N2—C13 | 117.71 (10) |
References
- Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K. & Puschmann, H. (2009). J. Appl. Cryst. 42, 339–341.
- Lassagne, F., Chevallier, F., Roisnel, T., Dorcet, V., Mongin, F. & Domingo, L. R. (2015). Synthesis, 47, 2680–2689.
- Rigaku (2018). CrysAlis PRO. Rigaku Inc., Tokyo, Japan.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S241431462000454X/hb4346sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S241431462000454X/hb4346Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S241431462000454X/hb4346Isup4.cml
Supplementary Material (FTIR, 1H NMR, 13C NMR). DOI: 10.1107/S241431462000454X/hb4346sup3.pdf
CCDC reference: 1994287
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




