The cationic ZnII part of aqua(1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane)zinc(II) diperchlorate, [Zn(C8H20N4)H2O](ClO4)2, exhibits a slightly distorted square-pyramidal coordination environment with a water molecule in the apical position.
Keywords: crystal structure, zinc(II) complex, cyclen
Abstract
The cationic ZnII part of aqua(1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane)zinc(II) bis(perchlorate), [Zn(C8H20N4)(H2O)](ClO4)2, exhibits a slightly distorted square-pyramidal coordination environment with a water molecule in the apical position. In the crystal, the macrocyclic ring alternates between two conformations with equal occupancies. Two of the three perchlorate anions are situated about a twofold rotation axis, and one of them shows disorder of the O atoms with occupancies of 0.62 (7) and 0.38 (7). In the crystal, the complexes are connected by intermolecular hydrogen bonding via the perchlorate anions.
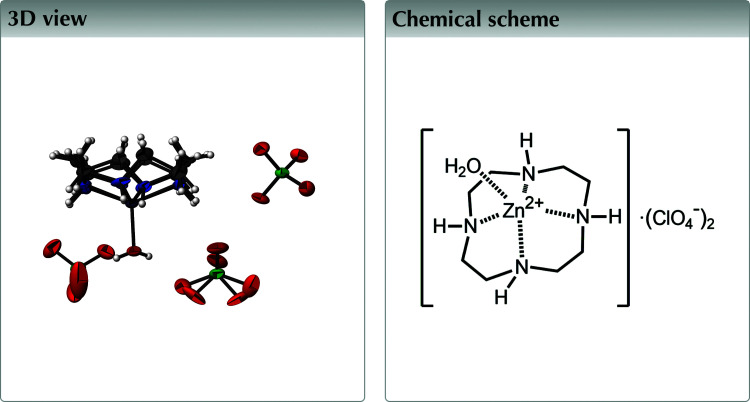
Structure description
The title complex, [Zn(C8H20N4)H2O](ClO4)2, comprises a cationic ZnII complex and three perchlorate anions, two of which are located about a twofold rotation axis with one of them disordered [occupancy ratio for the corresponding O atoms is 0.62 (7):0.38 (7)]. The macrocyclic ring is disordered, and two alternate conformations of each N–C–C–N bridge can be observed (conformation A and B) (Fig. 1 ▸), in which four carbon atoms (C2, C4, C6, and C8) are shared. The central ZnII cation is ligated by four N atoms of 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane (cyclen) in the basal plane, with a ZnII-bound H2O molecule occupying the apical position. Addison et al. (1984 ▸) proposed the geometry index [τ = (β − α)/60°] to determine if the five-coordinate atom has a square-pyramidal or trigonal–pyramidal coordination environment. The bond angles β and α are the largest and second-largest in the coordination sphere, respectively; an ideal square pyramid and an ideal trigonal bipyramid have τ = 0 and 1, respectively. In conformation A, the N—ZnII—N bond angles α and β are 138.2 (3)° and 138.7 (3)°, respectively; the corresponding bond angles in conformation B are 137.4 (4)° and138.7(4)°. The τ values are 0.008 and 0.022 for conformations A and B, respectively. Therefore, the coordination geometry around the central ZnII cation can be described as slightly distorted square-pyramidal. The occupancies for the non-hydrogen atoms of cyclen except for the four carbon atoms (C2, C4, C6, and C8) were set to 0.50. Atom Zn1 is 0.755 (5) and 0.763 (3) Å above the basal plane formed by four N atoms in conformations A and B, respectively. The Zn1—O1 bond length [1.9721 (4) Å] is within the typical range [1.94–2.03 Å] for similar five-coordinated Zn complexes (Bazzicalupi et al., 1995 ▸; Chen et al., 1994 ▸; Kato & Ito, 1985 ▸; Koike et al., 1994 ▸; Murthy & Karlin, 1993 ▸; Schrodt et al.; 1997 ▸). In addition, the mean Zn1—N bond length (2.13 Å) in the title complex is similar to that in the crystal structure of [Zn(cyclen)EtOH](ClO4)2 (Schrodt et al., 1997 ▸).
Figure 1.
The structures of the molecular entities within the title complex showing 50% displacement ellipsoids. [Symmetry codes: (i) −x + 1, y, −z +
 ; (ii) −x, y, −z +
; (ii) −x, y, −z +
 ].
].
The two perchlorate ions are involved in intermolecular hydrogen bonds with the cationic ZnII complex (Table 1 ▸). In the crystal, intermolecular hydrogen-bonding interactions connect neighboring molecules, forming a three-dimensional network (Fig. 2 ▸). As far as we know, an aqua(cyclen)copper(II) complex has already been reported (Pérez-Toro et al., 2015 ▸), but the aqua(cyclen)zinc(II) complex has not. The title aqua(cyclen)zinc(II) complex has been well studied as ZnII-containing enzyme models, such as alkaline phosphatase, β-lactamase, and carbonic anhydrase, to elucidate the essential roles of ZnII (Kimura et al., 1995 ▸; Kitajima et al., 1993 ▸; Zhang et al., 1993 ▸; Zhang & van Eldik, 1995 ▸). We succeeded in determining its crystal structure at this time.
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1—H1A⋯O9A | 0.86 | 2.48 | 3.12 (3) | 132 |
| O1—H1A⋯O9B | 0.86 | 1.94 | 2.68 (4) | 145 |
| O1—H1B⋯O6 | 0.85 | 2.06 | 2.914 (9) | 173 |
| O1—H1B⋯O7 | 0.85 | 2.54 | 3.088 (7) | 123 |
| N2A—H2A⋯O7 | 0.98 | 2.37 | 3.144 (12) | 135 |
| N2B—H2B⋯O4i | 0.98 | 2.49 | 3.086 (11) | 119 |
| N3A—H3A⋯O2ii | 0.98 | 2.59 | 3.312 (10) | 130 |
| N3B—H3B⋯O2ii | 0.98 | 2.47 | 3.170 (12) | 128 |
| N4A—H4A⋯O5iii | 0.98 | 2.18 | 3.094 (9) | 155 |
| N4A—H4A⋯O8iii | 0.98 | 2.49 | 3.103 (10) | 120 |
| N4B—H4B⋯O5iii | 0.98 | 2.1 | 3.030 (11) | 157 |
| N1A—H1AA⋯O8 | 0.98 | 2.15 | 3.099 (10) | 162 |
| N1B—H1BA⋯O8 | 0.98 | 2.16 | 3.105 (13) | 163 |
Symmetry codes: (i)
 ; (ii)
; (ii)
 ; (iii)
; (iii)
 .
.
Figure 2.
A view of the crystal packing of the title complex. Dashed lines denote the hydrogen bonds.
Synthesis and crystallization
The title complex was prepared as fine white solid according to a previously reported method (Koike et al., 1994 ▸) and then crystallized from aqueous ethanol.
Caution! Perchlorate salts of metal complexes with organic ligands are potentially explosive. Only small amounts of material should be prepared, and these should be handled with care.
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 2 ▸. In the final cycles of refinement, 12 outliers were omitted.
Table 2. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | [Zn(C8H20N4)(H2O)](ClO4)2 |
| M r | 454.56 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, P2/c |
| Temperature (K) | 93 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 12.3428 (6), 8.4603 (4), 16.0543 (6) |
| β (°) | 92.881 (4) |
| V (Å3) | 1674.33 (13) |
| Z | 4 |
| Radiation type | Cu Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 5.48 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.29 × 0.16 × 0.04 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Rigaku Synergy-i |
| Absorption correction | Gaussian (CrysAlis PRO; Rigaku OD, 2020 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.535, 1.000 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 7740, 3025, 2670 |
| R int | 0.057 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.603 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.067, 0.186, 1.08 |
| No. of reflections | 3025 |
| No. of parameters | 301 |
| H-atom treatment | H-atom parameters constrained |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 1.15, −0.84 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314621003977/vm4048sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314621003977/vm4048Isup2.hkl
CCDC reference: 2067247
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
full crystallographic data
Crystal data
| [Zn(C8H20N4)(H2O)](ClO4)2 | F(000) = 936 |
| Mr = 454.56 | Dx = 1.803 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P2/c | Cu Kα radiation, λ = 1.54184 Å |
| a = 12.3428 (6) Å | Cell parameters from 3951 reflections |
| b = 8.4603 (4) Å | θ = 5.5–68.1° |
| c = 16.0543 (6) Å | µ = 5.48 mm−1 |
| β = 92.881 (4)° | T = 93 K |
| V = 1674.33 (13) Å3 | Block, clear light colourless |
| Z = 4 | 0.29 × 0.16 × 0.04 mm |
Data collection
| Rigaku_Synergy-i diffractometer | 3025 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: micro-focus sealed X-ray tube, PhotonJet (Cu) X-ray Source | 2670 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Mirror monochromator | Rint = 0.057 |
| Detector resolution: 10.0000 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 68.4°, θmin = 3.6° |
| ω scans | h = −14→14 |
| Absorption correction: gaussian (CrysAlisPro; Rigaku OD, 2020) | k = −10→9 |
| Tmin = 0.535, Tmax = 1.000 | l = −19→8 |
| 7740 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: dual |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: mixed |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.067 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.186 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0991P)2 + 7.9372P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.08 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 3025 reflections | Δρmax = 1.15 e Å−3 |
| 301 parameters | Δρmin = −0.84 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. All hydrogen atoms were placed on calculated positions and refined in riding mode, with Uiso(H) values assigned as 1.2Ueq of the parent atoms (1.5 times for water molecule O1). |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | Occ. (<1) | |
| Zn1 | 0.26041 (6) | 0.65100 (8) | 0.40586 (4) | 0.0237 (3) | |
| Cl1 | 0.77745 (10) | 0.74888 (14) | 0.44398 (7) | 0.0253 (3) | |
| Cl3 | 0.500000 | 0.3592 (2) | 0.250000 | 0.0379 (5) | |
| Cl2 | 0.000000 | 0.4021 (3) | 0.250000 | 0.0427 (5) | |
| O2 | 0.8653 (4) | 0.6503 (5) | 0.4747 (3) | 0.0376 (10) | |
| O1 | 0.2571 (4) | 0.4307 (5) | 0.3658 (3) | 0.0380 (10) | |
| H1A | 0.288342 | 0.423897 | 0.319539 | 0.057* | |
| H1B | 0.191532 | 0.403407 | 0.353540 | 0.057* | |
| O5 | 0.6950 (4) | 0.6530 (4) | 0.4022 (2) | 0.0354 (10) | |
| O4 | 0.8158 (4) | 0.8651 (5) | 0.3871 (3) | 0.0386 (10) | |
| O3 | 0.7314 (4) | 0.8284 (5) | 0.5133 (3) | 0.0450 (11) | |
| O8 | 0.5265 (5) | 0.4556 (6) | 0.3200 (3) | 0.0565 (14) | |
| O7 | 0.0864 (5) | 0.4984 (7) | 0.2230 (3) | 0.0672 (17) | |
| C6 | 0.1725 (5) | 0.7292 (7) | 0.5681 (3) | 0.0337 (13) | |
| H6AA | 0.166719 | 0.628890 | 0.596708 | 0.040* | 0.5 |
| H6AB | 0.130034 | 0.806911 | 0.596576 | 0.040* | 0.5 |
| H6BC | 0.133141 | 0.634016 | 0.581254 | 0.040* | 0.5 |
| H6BD | 0.182279 | 0.791458 | 0.618632 | 0.040* | 0.5 |
| O9A | 0.430 (3) | 0.243 (3) | 0.2710 (8) | 0.066 (6) | 0.62 (7) |
| C8 | 0.4612 (5) | 0.7428 (8) | 0.5014 (4) | 0.0414 (15) | |
| H8AA | 0.487825 | 0.803166 | 0.549486 | 0.050* | 0.5 |
| H8AB | 0.512480 | 0.658178 | 0.492711 | 0.050* | 0.5 |
| H8BC | 0.524175 | 0.810202 | 0.510715 | 0.050* | 0.5 |
| H8BD | 0.479795 | 0.636990 | 0.520513 | 0.050* | 0.5 |
| C4 | 0.0710 (5) | 0.8437 (8) | 0.3503 (4) | 0.0392 (14) | |
| H4AA | 0.018566 | 0.760976 | 0.337036 | 0.047* | 0.5 |
| H4AB | 0.043655 | 0.941480 | 0.325667 | 0.047* | 0.5 |
| H4BC | 0.031273 | 0.783663 | 0.307339 | 0.047* | 0.5 |
| H4BD | 0.023943 | 0.927003 | 0.368971 | 0.047* | 0.5 |
| C2 | 0.3599 (6) | 0.8620 (7) | 0.2838 (4) | 0.0377 (14) | |
| H2AA | 0.351470 | 0.797633 | 0.233856 | 0.045* | 0.5 |
| H2AB | 0.412558 | 0.944234 | 0.274066 | 0.045* | 0.5 |
| H2BC | 0.399202 | 0.791877 | 0.248175 | 0.045* | 0.5 |
| H2BD | 0.352000 | 0.963274 | 0.255853 | 0.045* | 0.5 |
| N4A | 0.3533 (8) | 0.6720 (10) | 0.5194 (5) | 0.0214 (17) | 0.5 |
| H4A | 0.362285 | 0.569147 | 0.546981 | 0.026* | 0.5 |
| N2A | 0.1762 (9) | 0.8030 (13) | 0.3149 (5) | 0.0256 (18) | 0.5 |
| H2A | 0.163507 | 0.746012 | 0.262159 | 0.031* | 0.5 |
| N1A | 0.3988 (8) | 0.7609 (10) | 0.3570 (6) | 0.0238 (18) | 0.5 |
| H1AA | 0.446853 | 0.678514 | 0.336943 | 0.029* | 0.5 |
| N3A | 0.1304 (7) | 0.7131 (10) | 0.4792 (7) | 0.0243 (18) | 0.5 |
| H3A | 0.074948 | 0.630179 | 0.475250 | 0.029* | 0.5 |
| C3A | 0.2519 (10) | 0.9354 (13) | 0.3034 (6) | 0.028 (2) | 0.5 |
| H3AA | 0.259465 | 0.998537 | 0.353821 | 0.034* | 0.5 |
| H3AB | 0.225447 | 1.002771 | 0.257917 | 0.034* | 0.5 |
| C5A | 0.0848 (9) | 0.8626 (12) | 0.4440 (8) | 0.025 (2) | 0.5 |
| H5AA | 0.133508 | 0.949844 | 0.457747 | 0.030* | 0.5 |
| H5AB | 0.015347 | 0.884647 | 0.467187 | 0.030* | 0.5 |
| C7A | 0.2892 (10) | 0.7804 (15) | 0.5691 (7) | 0.027 (2) | 0.5 |
| H7AA | 0.293554 | 0.886458 | 0.546567 | 0.033* | 0.5 |
| H7AB | 0.319046 | 0.782356 | 0.626111 | 0.033* | 0.5 |
| C1A | 0.4564 (10) | 0.8461 (13) | 0.4278 (7) | 0.029 (2) | 0.5 |
| H1AB | 0.529179 | 0.873893 | 0.413020 | 0.034* | 0.5 |
| H1AC | 0.417900 | 0.942758 | 0.439999 | 0.034* | 0.5 |
| N1B | 0.4265 (8) | 0.7403 (14) | 0.4110 (8) | 0.034 (2) | 0.5 |
| H1BA | 0.471976 | 0.663912 | 0.382960 | 0.041* | 0.5 |
| C1B | 0.4205 (10) | 0.8823 (15) | 0.3617 (8) | 0.037 (3) | 0.5 |
| H1BB | 0.386928 | 0.964996 | 0.393325 | 0.045* | 0.5 |
| H1BC | 0.493463 | 0.916393 | 0.350715 | 0.045* | 0.5 |
| N4B | 0.2823 (11) | 0.6851 (12) | 0.5371 (6) | 0.033 (2) | 0.5 |
| H4B | 0.308024 | 0.586973 | 0.563809 | 0.040* | 0.5 |
| C7B | 0.3640 (11) | 0.8079 (15) | 0.5489 (7) | 0.037 (3) | 0.5 |
| H7BA | 0.383889 | 0.822821 | 0.607646 | 0.044* | 0.5 |
| H7BB | 0.338491 | 0.907531 | 0.525404 | 0.044* | 0.5 |
| N3B | 0.1035 (9) | 0.7343 (14) | 0.4242 (7) | 0.039 (3) | 0.5 |
| H3B | 0.052515 | 0.645734 | 0.426759 | 0.047* | 0.5 |
| C5B | 0.1084 (10) | 0.8221 (16) | 0.5035 (8) | 0.037 (3) | 0.5 |
| H5BA | 0.035586 | 0.839754 | 0.521684 | 0.044* | 0.5 |
| H5BB | 0.142278 | 0.924175 | 0.495850 | 0.044* | 0.5 |
| N2B | 0.2492 (10) | 0.7937 (12) | 0.2972 (6) | 0.033 (2) | 0.5 |
| H2B | 0.224070 | 0.730603 | 0.248759 | 0.039* | 0.5 |
| C3B | 0.1686 (14) | 0.914 (2) | 0.3155 (7) | 0.044 (3) | 0.5 |
| H3BA | 0.147684 | 0.971106 | 0.264677 | 0.053* | 0.5 |
| H3BB | 0.200630 | 0.989686 | 0.355062 | 0.053* | 0.5 |
| O9B | 0.384 (3) | 0.296 (5) | 0.255 (3) | 0.066 (12) | 0.38 (7) |
| O6 | 0.0412 (6) | 0.3127 (13) | 0.3175 (6) | 0.138 (5) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Zn1 | 0.0349 (4) | 0.0181 (4) | 0.0184 (4) | −0.0015 (3) | 0.0045 (3) | −0.0025 (2) |
| Cl1 | 0.0352 (7) | 0.0198 (6) | 0.0207 (6) | −0.0012 (5) | 0.0004 (5) | −0.0014 (4) |
| Cl3 | 0.0561 (13) | 0.0208 (9) | 0.0381 (11) | 0.000 | 0.0146 (9) | 0.000 |
| Cl2 | 0.0591 (13) | 0.0369 (11) | 0.0334 (10) | 0.000 | 0.0138 (9) | 0.000 |
| O2 | 0.041 (2) | 0.033 (2) | 0.039 (2) | 0.0041 (18) | 0.0003 (18) | 0.0095 (17) |
| O1 | 0.052 (3) | 0.024 (2) | 0.040 (2) | −0.0067 (19) | 0.0189 (19) | −0.0098 (17) |
| O5 | 0.049 (3) | 0.023 (2) | 0.032 (2) | −0.0112 (17) | −0.0131 (18) | 0.0006 (15) |
| O4 | 0.058 (3) | 0.029 (2) | 0.029 (2) | −0.0082 (19) | 0.0013 (18) | 0.0091 (16) |
| O3 | 0.056 (3) | 0.041 (2) | 0.039 (2) | −0.003 (2) | 0.018 (2) | −0.0173 (19) |
| O8 | 0.071 (3) | 0.031 (2) | 0.064 (3) | 0.009 (2) | −0.020 (3) | −0.017 (2) |
| O7 | 0.089 (4) | 0.059 (3) | 0.057 (3) | −0.030 (3) | 0.036 (3) | −0.019 (3) |
| C6 | 0.054 (4) | 0.026 (3) | 0.023 (3) | 0.003 (3) | 0.016 (2) | −0.003 (2) |
| O9A | 0.089 (13) | 0.052 (8) | 0.053 (6) | −0.048 (8) | −0.021 (6) | 0.024 (6) |
| C8 | 0.042 (3) | 0.050 (4) | 0.032 (3) | 0.004 (3) | −0.003 (3) | −0.013 (3) |
| C4 | 0.042 (3) | 0.038 (3) | 0.036 (3) | 0.008 (3) | −0.008 (3) | −0.010 (3) |
| C2 | 0.056 (4) | 0.032 (3) | 0.027 (3) | −0.004 (3) | 0.014 (3) | 0.007 (2) |
| N4A | 0.026 (5) | 0.015 (4) | 0.024 (4) | 0.008 (4) | 0.003 (4) | 0.000 (3) |
| N2A | 0.039 (6) | 0.021 (6) | 0.017 (4) | −0.007 (5) | 0.003 (4) | −0.004 (4) |
| N1A | 0.030 (5) | 0.016 (5) | 0.026 (5) | 0.002 (4) | 0.003 (4) | 0.001 (4) |
| N3A | 0.030 (5) | 0.015 (5) | 0.028 (5) | 0.004 (4) | 0.000 (4) | −0.006 (4) |
| C3A | 0.042 (7) | 0.027 (6) | 0.016 (5) | −0.001 (5) | −0.003 (4) | −0.002 (4) |
| C5A | 0.023 (5) | 0.016 (5) | 0.036 (7) | 0.003 (4) | 0.000 (4) | −0.006 (4) |
| C7A | 0.036 (7) | 0.027 (6) | 0.019 (5) | 0.004 (5) | 0.000 (5) | −0.001 (5) |
| C1A | 0.039 (6) | 0.013 (5) | 0.035 (7) | −0.012 (5) | 0.009 (5) | −0.008 (4) |
| N1B | 0.022 (5) | 0.044 (8) | 0.037 (6) | 0.005 (5) | 0.002 (4) | −0.001 (5) |
| C1B | 0.040 (7) | 0.035 (7) | 0.038 (7) | −0.014 (5) | 0.018 (5) | −0.007 (5) |
| N4B | 0.068 (9) | 0.013 (5) | 0.019 (5) | 0.011 (5) | 0.000 (5) | 0.002 (4) |
| C7B | 0.046 (8) | 0.035 (7) | 0.028 (6) | 0.007 (6) | −0.009 (5) | −0.008 (5) |
| N3B | 0.035 (6) | 0.046 (7) | 0.037 (7) | −0.010 (5) | 0.010 (5) | −0.011 (5) |
| C5B | 0.037 (6) | 0.036 (7) | 0.038 (7) | −0.005 (5) | 0.013 (5) | −0.005 (6) |
| N2B | 0.052 (7) | 0.028 (5) | 0.018 (4) | 0.006 (5) | −0.002 (4) | −0.002 (4) |
| C3B | 0.072 (12) | 0.035 (9) | 0.024 (6) | 0.008 (7) | −0.014 (6) | −0.002 (5) |
| O9B | 0.071 (17) | 0.073 (17) | 0.056 (18) | −0.027 (15) | 0.028 (13) | −0.040 (13) |
| O6 | 0.074 (5) | 0.188 (10) | 0.156 (8) | 0.037 (6) | 0.033 (5) | 0.136 (8) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Zn1—O1 | 1.971 (4) | C6—C7A | 1.503 (14) |
| Zn1—N4A | 2.111 (9) | C6—N4B | 1.513 (14) |
| Zn1—N2A | 2.171 (10) | C6—C5B | 1.495 (15) |
| Zn1—N1A | 2.129 (9) | C8—N4A | 1.501 (12) |
| Zn1—N3A | 2.104 (9) | C8—C1A | 1.468 (13) |
| Zn1—N1B | 2.183 (10) | C8—N1B | 1.492 (13) |
| Zn1—N4B | 2.130 (10) | C8—C7B | 1.555 (15) |
| Zn1—N3B | 2.096 (11) | C4—N2A | 1.484 (13) |
| Zn1—N2B | 2.121 (9) | C4—C5A | 1.514 (13) |
| Cl1—O2 | 1.436 (4) | C4—N3B | 1.542 (14) |
| Cl1—O5 | 1.440 (4) | C4—C3B | 1.479 (19) |
| Cl1—O4 | 1.438 (4) | C2—N1A | 1.512 (12) |
| Cl1—O3 | 1.442 (4) | C2—C3A | 1.519 (14) |
| Cl3—O8i | 1.413 (5) | C2—C1B | 1.435 (15) |
| Cl3—O8 | 1.413 (5) | C2—N2B | 1.510 (14) |
| Cl3—O9A | 1.364 (14) | N4A—C7A | 1.472 (14) |
| Cl3—O9Ai | 1.364 (14) | N2A—C3A | 1.476 (15) |
| Cl3—O9B | 1.53 (3) | N1A—C1A | 1.496 (15) |
| Cl3—O9Bi | 1.53 (3) | N3A—C5A | 1.485 (14) |
| Cl2—O7ii | 1.427 (5) | N1B—C1B | 1.439 (17) |
| Cl2—O7 | 1.427 (5) | N4B—C7B | 1.454 (18) |
| Cl2—O6ii | 1.397 (7) | N3B—C5B | 1.473 (16) |
| Cl2—O6 | 1.397 (7) | N2B—C3B | 1.466 (18) |
| C6—N3A | 1.500 (12) | ||
| O1—Zn1—N4A | 111.3 (3) | O6—Cl2—O7 | 107.3 (5) |
| O1—Zn1—N2A | 109.8 (3) | O6—Cl2—O6ii | 114.4 (11) |
| O1—Zn1—N1A | 107.2 (3) | N3A—C6—C7A | 108.8 (6) |
| O1—Zn1—N3A | 114.5 (3) | C5B—C6—N4B | 110.7 (7) |
| O1—Zn1—N1B | 110.1 (3) | C1A—C8—N4A | 113.1 (7) |
| O1—Zn1—N4B | 116.8 (3) | N1B—C8—C7B | 107.0 (7) |
| O1—Zn1—N3B | 111.1 (3) | N2A—C4—C5A | 110.4 (7) |
| O1—Zn1—N2B | 105.7 (3) | C3B—C4—N3B | 110.4 (7) |
| N4A—Zn1—N2A | 138.7 (3) | N1A—C2—C3A | 108.5 (6) |
| N4A—Zn1—N1A | 82.6 (4) | C1B—C2—N2B | 111.0 (7) |
| N1A—Zn1—N2A | 81.9 (4) | C8—N4A—Zn1 | 108.4 (5) |
| N3A—Zn1—N4A | 83.8 (4) | C7A—N4A—Zn1 | 103.7 (7) |
| N3A—Zn1—N2A | 82.9 (4) | C7A—N4A—C8 | 111.2 (8) |
| N3A—Zn1—N1A | 138.2 (3) | C4—N2A—Zn1 | 106.2 (5) |
| N4B—Zn1—N1B | 81.0 (5) | C3A—N2A—Zn1 | 104.4 (7) |
| N3B—Zn1—N1B | 138.7 (4) | C3A—N2A—C4 | 116.3 (10) |
| N3B—Zn1—N4B | 83.6 (5) | C2—N1A—Zn1 | 107.7 (6) |
| N3B—Zn1—N2B | 84.4 (5) | C1A—N1A—Zn1 | 106.8 (7) |
| N2B—Zn1—N1B | 81.8 (5) | C1A—N1A—C2 | 116.0 (8) |
| N2B—Zn1—N4B | 137.4 (4) | C6—N3A—Zn1 | 108.5 (5) |
| O2—Cl1—O5 | 109.7 (3) | C5A—N3A—Zn1 | 106.5 (7) |
| O2—Cl1—O4 | 110.4 (3) | C5A—N3A—C6 | 113.0 (8) |
| O2—Cl1—O3 | 109.0 (3) | N2A—C3A—C2 | 106.4 (9) |
| O5—Cl1—O3 | 109.0 (3) | N3A—C5A—C4 | 108.1 (8) |
| O4—Cl1—O5 | 109.7 (2) | N4A—C7A—C6 | 110.8 (10) |
| O4—Cl1—O3 | 109.1 (3) | C8—C1A—N1A | 108.8 (9) |
| O8—Cl3—O8i | 109.5 (4) | C8—N1B—Zn1 | 105.3 (6) |
| O8i—Cl3—O9B | 94 (3) | C1B—N1B—Zn1 | 104.2 (8) |
| O8—Cl3—O9B | 109.6 (8) | C1B—N1B—C8 | 121.9 (10) |
| O8—Cl3—O9Bi | 94 (3) | C2—C1B—N1B | 112.9 (10) |
| O8i—Cl3—O9Bi | 109.6 (8) | C6—N4B—Zn1 | 106.7 (6) |
| O9A—Cl3—O8 | 110.2 (8) | C7B—N4B—Zn1 | 106.2 (8) |
| O9Ai—Cl3—O8 | 119.3 (9) | C7B—N4B—C6 | 114.0 (10) |
| O9Ai—Cl3—O8i | 110.2 (8) | N4B—C7B—C8 | 103.3 (9) |
| O9A—Cl3—O8i | 119.3 (9) | C4—N3B—Zn1 | 107.4 (6) |
| O9Ai—Cl3—O9A | 88 (3) | C5B—N3B—Zn1 | 107.0 (8) |
| O9Ai—Cl3—O9Bi | 29.6 (13) | C5B—N3B—C4 | 111.1 (10) |
| O9A—Cl3—O9Bi | 112 (3) | N3B—C5B—C6 | 109.3 (11) |
| O7—Cl2—O7ii | 110.4 (5) | C2—N2B—Zn1 | 108.2 (6) |
| O6ii—Cl2—O7ii | 107.3 (5) | C3B—N2B—Zn1 | 104.4 (8) |
| O6ii—Cl2—O7 | 108.8 (5) | C3B—N2B—C2 | 113.0 (10) |
| O6—Cl2—O7ii | 108.8 (5) | N2B—C3B—C4 | 111.6 (13) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, y, −z+1/2; (ii) −x, y, −z+1/2.
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O1—H1A···O9A | 0.86 | 2.48 | 3.12 (3) | 132 |
| O1—H1A···O9B | 0.86 | 1.94 | 2.68 (4) | 145 |
| O1—H1B···O6 | 0.85 | 2.06 | 2.914 (9) | 173 |
| O1—H1B···O7 | 0.85 | 2.54 | 3.088 (7) | 123 |
| N2A—H2A···O7 | 0.98 | 2.37 | 3.144 (12) | 135 |
| N2B—H2B···O4i | 0.98 | 2.49 | 3.086 (11) | 119 |
| N3A—H3A···O2iii | 0.98 | 2.59 | 3.312 (10) | 130 |
| N3B—H3B···O2iii | 0.98 | 2.47 | 3.170 (12) | 128 |
| N4A—H4A···O5iv | 0.98 | 2.18 | 3.094 (9) | 155 |
| N4A—H4A···O8iv | 0.98 | 2.49 | 3.103 (10) | 120 |
| N4B—H4B···O5iv | 0.98 | 2.1 | 3.030 (11) | 157 |
| N1A—H1AA···O8 | 0.98 | 2.15 | 3.099 (10) | 162 |
| N1B—H1BA···O8 | 0.98 | 2.16 | 3.105 (13) | 163 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, y, −z+1/2; (iii) x−1, y, z; (iv) −x+1, −y+1, −z+1.
References
- Addison, W. A., Rao, N. T., Reedijk, J., van Rijn, J. & Verschoor, C. G. (1984). J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. pp. 1349–1356.
- Bazzicalupi, C., Bencini, A., Bianchi, A., Fusi, V., Paoletti, P. & Valtancoli, B. (1995). J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. pp. 1555–1556.
- Chen, X.-M., Deng, Q.-Y., Wang, G. & Xu, Y.-J. (1994). Polyhedron, 13, 3085–3089.
- Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K. & Puschmann, H. (2009). J. Appl. Cryst. 42, 339–341.
- Kato, M. & Ito, T. (1985). Inorg. Chem. 24, 509–514.
- Kimura, E., Kodama, Y., Koike, T. & Shiro, M. (1995). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 117, 8304–8311.
- Kitajima, N., Hikichi, S., Tanaka, M. & Morooka, Y. (1993). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 115, 5496–5508.
- Koike, T., Takamura, M. & Kimura, E. (1994). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 116, 8443–8449.
- Murthy, N. N. & Karlin, K. D. (1993). J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. pp. 1236–1238.
- Pérez-Toro, I., Domínguez-Martín, A., Choquesillo-Lazarte, D., Vílchez-Rodríguez, E., González-Pérez, J. M., Castiñeiras, A. & Niclós-Gutiérrez, J. (2015). J. Inorg. Biochem. 148, 84–92. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Rigaku OD (2020). CrysAlis PRO. Rigaku Oxford Diffraction, Yarnton, England.
- Schrodt, A., Neubrand, A. & van Eldik, R. (1997). Inorg. Chem. 36, 4579–4584. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015a). Acta Cryst. A71, 3–8.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015b). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Zhang, X. & van Eldik, R. (1995). Inorg. Chem. 34, 5606–5614.
- Zhang, X., van Eldik, R., Koike, T. & Kimura, E. (1993). Inorg. Chem. 32, 5749–5755.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314621003977/vm4048sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314621003977/vm4048Isup2.hkl
CCDC reference: 2067247
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




