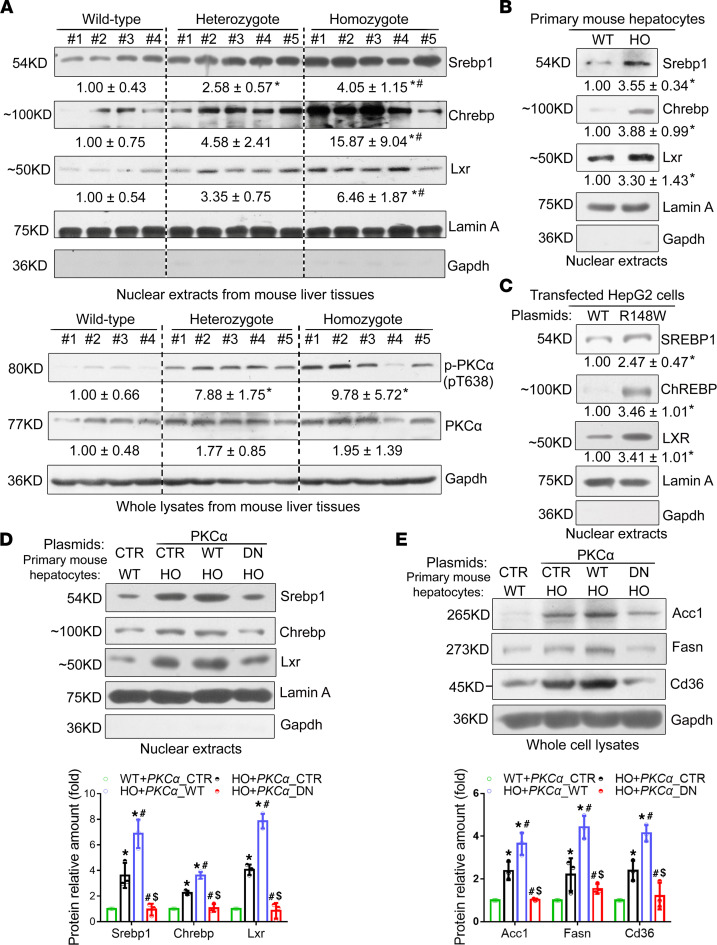
Figure 5. The Sema7aR145W mutation enhances hepatic FA and TG synthesis and FA uptake by enhancing PKC-α signaling–stimulated expression of transcription factors Srebp1 and Chrebp and nuclear receptor Lxr.
(A) Western blot analysis of the relative levels of Srebp1, Chrebp, Lxr, phosphorylated PKC-α, and PKC-α protein expression in 10-week-old male WT mice (n = 4), Sema7aR145W heterozygous mice (n = 5), and Sema7aR145W homozygous mice (n = 5). Western blot analysis of the relative levels of nuclear Srebp1, Chrebp, and Lxr proteins in primary hepatocytes from WT and Sema7aR145W homozygous mice (B) and in human hepatoma HepG2 cells (C) after transfection with the plasmid for the expression of SEMA7A_WT and SEMA7A_R148W proteins. (D) Representative Western blot of the relative levels of nuclear Srebp1, Chrebp, and Lxr proteins in nuclear extracts and (E) Fasn, Acc1, and Cd36 proteins in whole-cell lysates of primary mouse hepatocytes after transfection with empty vector (CTR) or the plasmid for the expression of PKCα_WT or PKCα_dominant negative (DN) mutant, respectively. All primary mouse hepatocytes were isolated from 12-week-old male WT and Sema7aR145W homozygous mice. Data are representative images or expressed as the mean ± SD of each group from 3 separate experiments. The data were analyzed by 1-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc tests or by Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s post hoc test analysis. *P < 0.05 versus the WT mice, #P < 0.05 versus the Sema7aR145W heterozygous mice, $P < 0.05 versus the primary HO mouse hepatocytes transfected with CTR; n = 3.