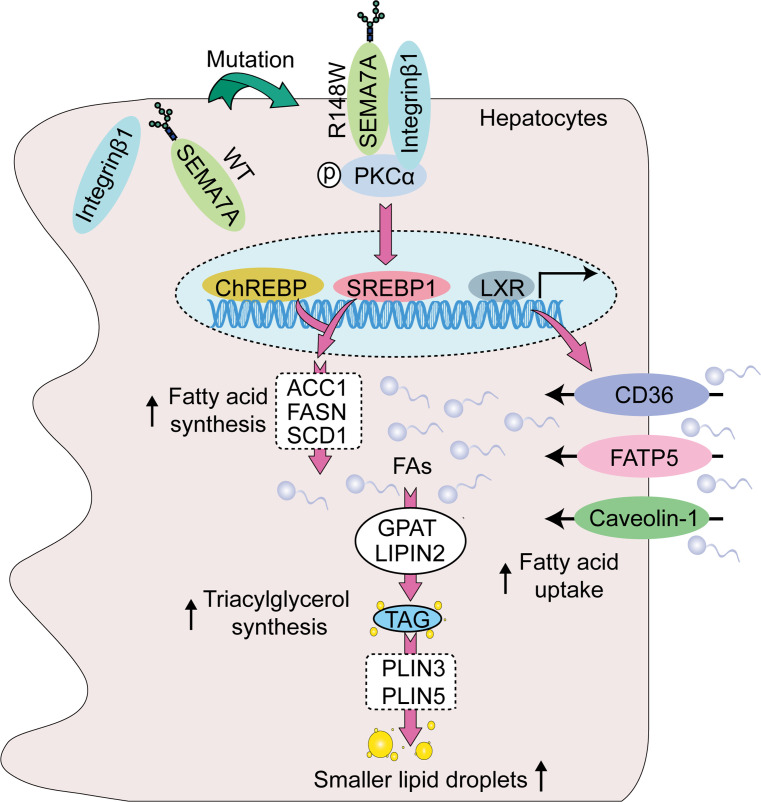
Figure 8. The potential mechanism by which the SEMA7AR148W mutation causes lipid accumulation in hepatocytes.
First, the mutation increases SEMA7A and its receptor integrin β1 proteins on the surface of cell membranes to promote PKC-α activation in hepatocytes. Second, the activated PKC-α signaling enhances the expression of transcriptional factors SREBP1 and ChREBP and nuclear receptor LXR, increasing FA and TG synthesis and FA uptake in hepatocytes. Finally, these increased the accumulation of small lipid droplets in the liver, leading to the development and progression of NAFLD.