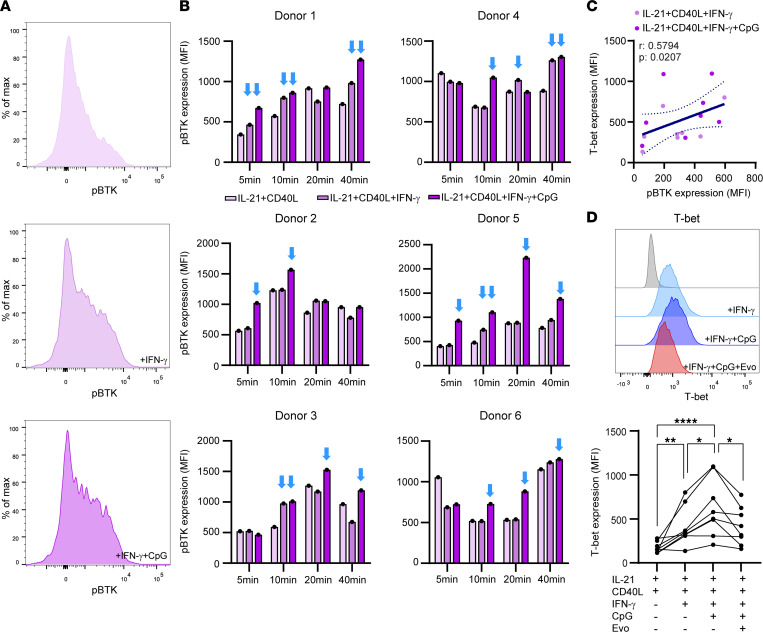
Figure 3. BTK activity is associated with IFN-γ– and CpG-mediated T-bet induction in human B cells.
(A) Representative histograms of phospho-BTK expression in healthy blood-derived B cells stimulated with IL-21+CD40L, IL-21+CD40L+IFN-γ, and IL-21+CD40L+IFN-γ+CpG for 10 minutes. (B) Donor-specific phospho-BTK induction in blood B cells under the same conditions for 5, 10, 20, and 40 minutes (n = 6). The blue arrows indicate time points at which phospho-BTK is upregulated by IFN-γ with and without CpG. These FACS data were collected in 4 independent experiments, with 1–2 donors per experiment. (C) Correlation between phospho-BTK and T-bet levels in B cells under IL-21/CD40L/IFN-γ–inducing conditions with and without CpG for 48 hours. (D) The effect of evobrutinib (Evo) on IFN-γ– and CpG-induced T-bet expression in B cells (48 hours). These data were collected in 3 independent experiments, with 2 –3 donors per experiment. (C) Spearman’s correlation and (D) repeated measures 1-way ANOVA with Fisher’s least significant difference post hoc test was performed. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ****P < 0.0001.