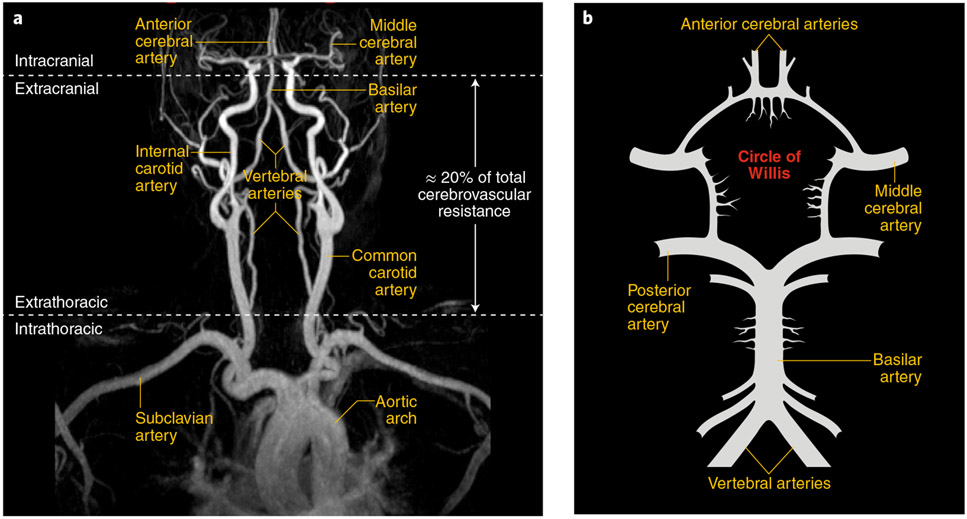
Fig. 1 ∣. Anatomy of the large vessels supplying the brain.
a, Common carotid arteries arise from large intrathoracic arteries and give rise to the internal carotid arteries that enter the skull and merge into the circle of Willis. Vertebral arteries run along the cervical vertebrae and enter the skull and join to form the basilar artery, which merges into the circle of Willis. On the basis of AP gradient measurements, extracranial arteries are responsible for ~20% of the total cerebrovascular resistance34, which suggests that they contribute to the regulation of cerebral perfusion. b, Schematic representation of the circle of Willis and its major branches. Image provided by A. Gupta.