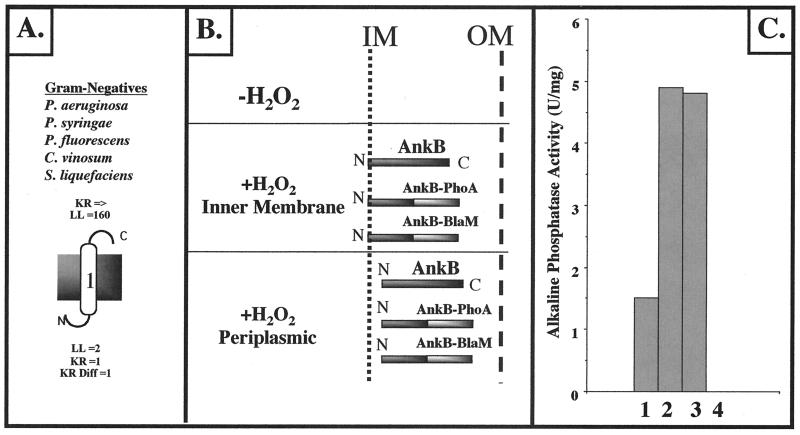
FIG. 3.
Cellular localization of AnkB in P. aeruginosa. (A) Predicted cytoplasmic membrane organization of P. aeruginosa AnkB bacterial ankyrin-like proteins from P. syringae, P. fluorescens, S. liquefaciens, and C. vinosum based upon the positive-inside-rule algorithm developed by von Heijne (57). For the P. aeruginosa AnkB protein, the large number 1 indicates the predicted single MSD. N, N terminus; C, C terminus; LL, loop length; KR, number of lysine and arginine residues; KR Diff, positive charge difference. (B) Schematic diagram of AnkB–β-lactamase and AnkB-PhoA protein fusions in both E. coli and P. aeruginosa PAO1. In both cases, organisms expressing AnkB–β-lactamase were resistant to ampicillin (E. coli) or carbenicillin (P. aeruginosa). Organisms expressing AnkB-PhoA were found to hydrolyze the alkaline phosphatase substrate BCIP in L-agar plates. IM, inner membrane; OM, outer membrane. (C) AP activity in cellular fractions of P. aeruginosa ankB harboring pEX30-ankB::phoA. Bar 1, cytoplasm; bar 2, periplasm; bar 3, cytoplasmic membrane; bar 4, outer membrane.