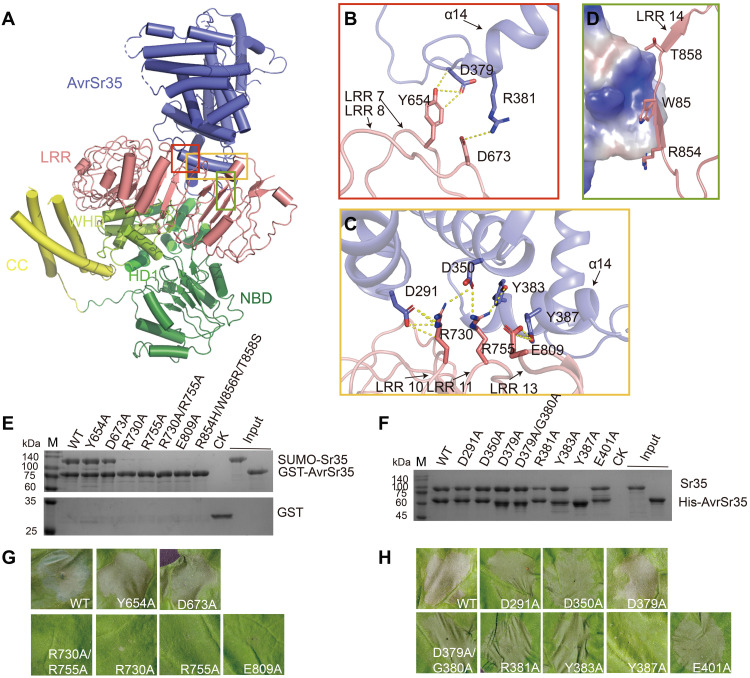
Fig. 3. The C-terminal LRR domain mediates Sr35 interaction with AvrSr35.
(A) Overall structure of Sr35-AvrSr35 complex in resistosome shown in cartoon mode. The interaction regions between the two proteins are highlighted with different colored frames. (B) Detailed interactions of the N terminus of the AvrSr35 helix α14 with Sr35 LRRs 7 and 8. Hydrogen bonds are shown as yellow dashed lines. (C) Detailed interactions of AvrSr35 α14 with Sr35 LRRs 11 and 13. Hydrogen bonds are shown as yellow dashed lines. (D) Surface contacts between the R854, W856, and T858 of Sr35LRR, as well as AvrSr35, represented by its coulombic surface potential. (E) Sr35 or (F) AvrSr35 mutations reduce Sr35-AvrSr35 interaction in vitro. Purified N-terminal 6×His-SUMO–tagged WT or mutant Sr35 was incubated with GST-tagged AvrSr35, or Sr35 was incubated with 6×His-tagged WT or mutant AvrSr35, followed by purification using Glutathione Sepharose 4B or Ni–nitrilotriacetic acid (Ni-NTA) beads. The proteins were visualized by SDS-PAGE with Coomassie brilliant blue staining. CK in (E), control containing GST protein and SUMO-Sr35; CK in (F), control group containing Sr35. (G) Sr35 or (H) AvrSr35 mutations abolish disease resistance in N. benthamiana leaves. The images were taken at 36 to 48 hpi. The experiment was performed three times.