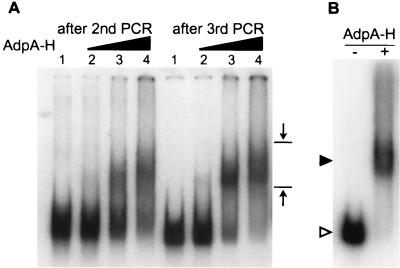
FIG. 2.
Gel mobility shift-PCR for isolation of DNA fragments recognized and bound by AdpA-H (A) and gel mobility shift of AdBS1 caused by AdpA-H (B). (A) The S. griseus chromosomal DNA of 300 to 500 bp obtained after HaeIII digestion was sandwiched by the catch linkers, 32P-labeled, mixed and incubated with AdpA-H, and run on a polyacrylamide gel. The amounts of AdpA-H used were 0.02 μg (lane 2), 0.2 μg (lane 3), and 1 μg (lane 4). Lane 1 is a control lane in which there was no AdpA-H. The DNA fragments retarded were recovered and subjected to a second cycle and further cycles. The mobility shift patterns after the second and third cycles are presented, showing the presence of retarded signals. The opposing arrows show the area from which DNA was extracted; the upper position was determined with a 500-bp DNA fragment, including the AdpA-binding site for strR, and the lower position was determined with a 300-bp fragment including the same AdpA-binding site, as described in Materials and Methods. (B) AdBS1 was excised by EcoRI digestion of the recombinant pUC19 plasmid, 32P-labeled, and subjected to gel mobility shift assay. In the presence of AdpA-H (0.2 μg), AdBS1 is shifted. The positions of AdpA-H-bound (solid triangle) and free (open triangle) probes are shown.