Fig. 1.
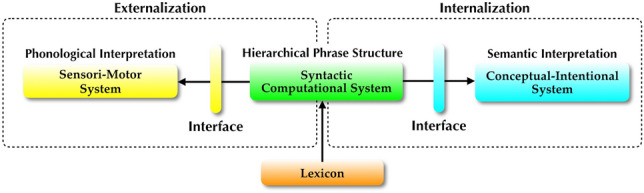
Basic architecture of the human language faculty. The lexicon provides inputs to the syntactic computational system (syntax), which combines these lexical items into a hierarchical phrase structure. This structure is then transferred to the two interpretive systems, the conceptual-intentional (CI) system for semantic interpretation and the sensorimotor (SM) system for phonological interpretation, including signs and other forms of surface realizations, via the two interfaces which roughly correspond to Logical Form (LF) and Phonetic Form (PF) in earlier versions of generative grammar. The syntax-CI connection is adaptive for internalization that takes place within an individual (thought, inference, planning, etc.), while the syntax-SM connection is for externalization (communication with other individuals)
