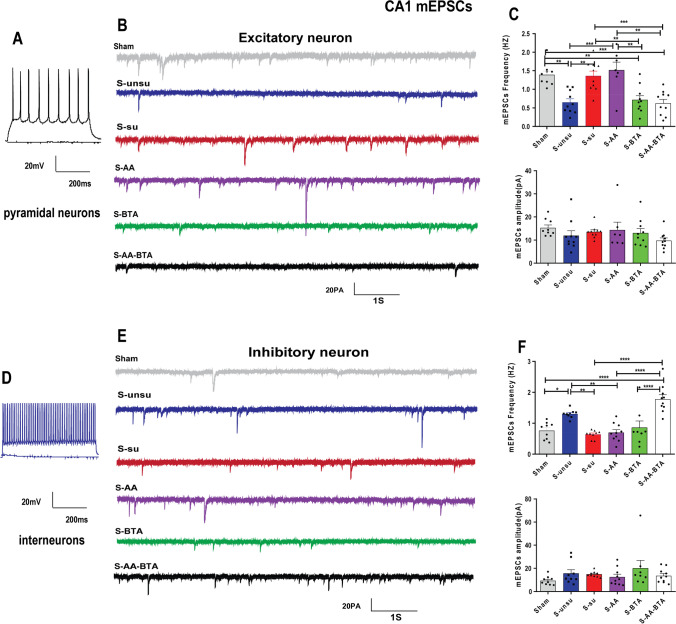
Fig. 9.
SCFA treatment restored synaptic deficits in hippocampal CA1 neurons in cognitively compromised pain rats. A–C Effect of the SCFA intervention on the spontaneous synaptic transmission of excitatory neurons in hippocampal CA1 slices neurons. A Current-clamp recordings to identify excitatory neurons in the hippocampal CA1. B Representative mEPSC recording traces from the six groups. C Bar graphs showing the frequency and the amplitude of mEPSCs in hippocampal CA1 excitatory neurons. N = 5 rats for each group. D–F Effect of the SCFA intervention on the spontaneous synaptic transmission of hippocampal CA1 inhibitory neurons. D Current-clamp recordings to identify inhibitory neurons in the hippocampal CA1. E Representative mEPSCs of inhibitory neurons recording traces from the six groups. F Bar graphs showing the frequency and the amplitude of mEPSCs in hippocampal CA1 inhibitory neurons. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM; n = 5 rats for each group. Tukey’s post hoc tests; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001