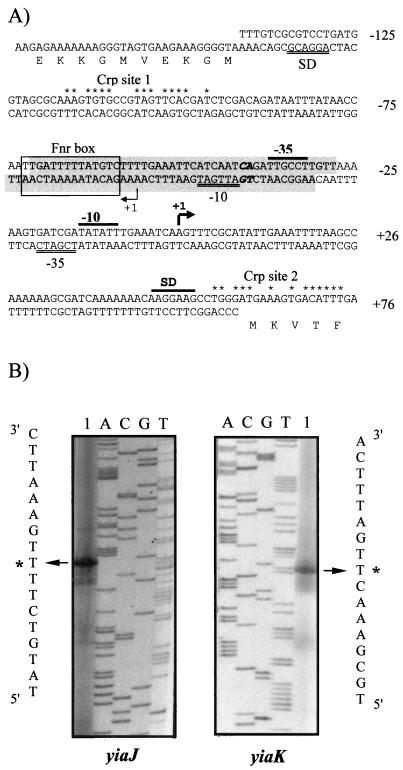
FIG. 3.
Promoter sequences and primer extension analysis of the divergently transcribed yiaK and yiaJ genes. (A) The sequence containing both overlapping promoters is presented and numbered relative to the 5′ end of the yiaK gene. For each gene, the Shine-Dalgarno sequences (SD) and the −10 and −35 consensus for RNA polymerase binding are indicated by a double underline for yiaJ and a black bar for yiaK. Nucleotides in the extension of the −10 consensus for yiaJ are shown in boldface. The 5′ ends are shown by arrowheads labeled as +1. Potential IHF binding sites, identified by using the MacTargsearch program (10), are shaded. The putative Fnr site is boxed, and positions conserved with respect to the Crp consensus (7) in Crp putative sites are indicated by asterisks. (B) The primed-extended products using total RNA of strain ECL1 (lane 1 of the yiaJ panel) or strain JA134 (lane 1 of the yiaK panel) were electrophoresed with a sequencing ladder (lanes A, C, G, and T) generated by using the same template and primer. A portion of the nucleotide sequence deduced from the sequencing lanes is shown. The most intense extended product assigned as the transcriptional start site for each gene is labeled by an asterisk.