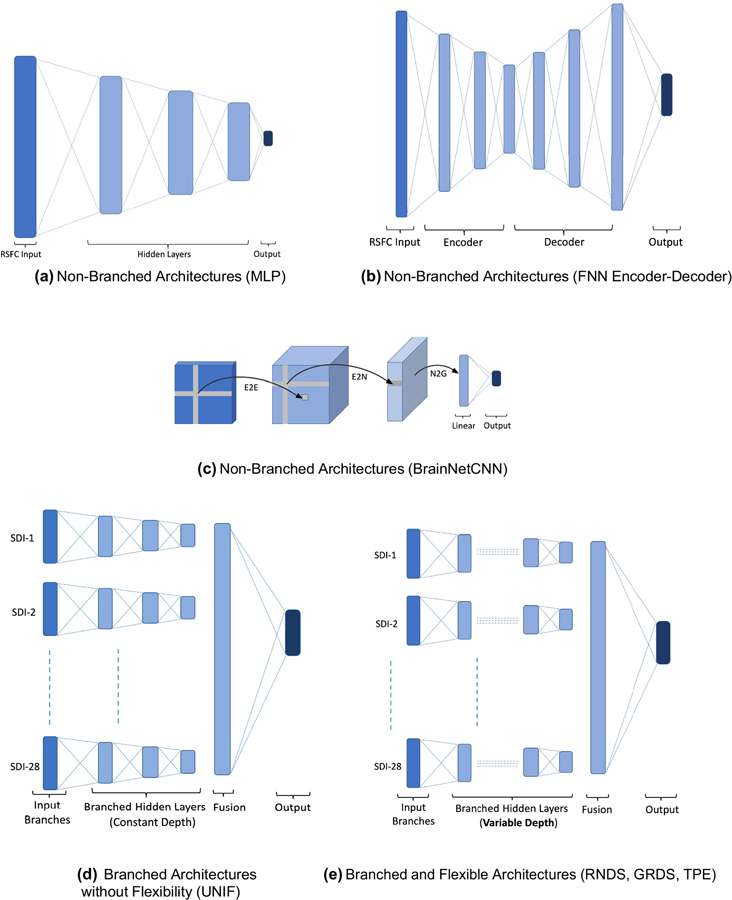
Figure 3.
A schematic diagram for neural network based methods used for performance comparison with the TPE based approach. In addition to standard machine learning models like SVM, logistic regression (LOG) and random forest classifier (RFC), baseline non-branched neural network architectures used were (a) multilayer perceptron (MLP), (b) feedforward neural network with encoder-decoder architecture (FNN) and (c) BrainNetCNN. Branched neural network architectures included (d) uniform architectures, UNIF0, UNIF1 and UNIF2, representing non-flexible multi-branched architectures with 0, 1 and 2 fully connected layers before the fusion step and above input layer in each SDI branch of the architecture respectively. (e) As the third baseline neural network methods, existing hyper-parameter optimization techniques including random search (RNDS) and grid search (GRDS) were used to optimize the domain of branched architectures with variable branch-depth, representing the same class as TPE.