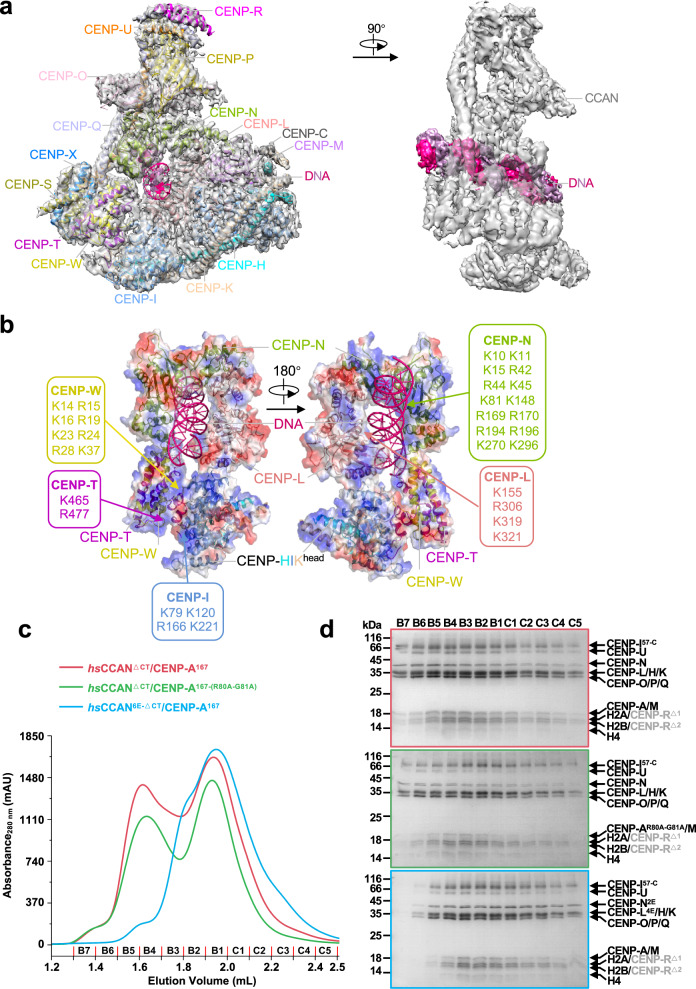
Fig. 2. DNA binds to CCAN through the CENP-LN channel.
a The 3.7 Å resolution cryo-EM density map of CCAN–DNA complex at two different views. The density map of DNA is colored by hotpink and the others are shown in gray transparent surfaces. b Electrostatic potential surface view of CENP-LN-HIKhead-TW binding with DNA. The DNA is shown as cartoon. Note that positively charged amino acids from CENP-LN, CENP-I and CENP-TW constitute the contact sites between CCAN and DNA. c, d Comparison of elution profiles (c) of CCANΔCT-CENP-A167/CCANΔCT-CENP-A167-(R80A-G81A) and CCAN6E-ΔCT-CENP-A167 in Superose 6 5/150 GL (GE Health) and the Coomassie-blue stained 15% SDS-PAGE gel. CENP-A167 is the CENP-A nucleosome reconstituted by using a DNA fragment of 167 bp in length. d The CCANΔCT complex bound to either CENP-A nucleosome or CENP-AR80A-G81A nucleosome which reconstituted with 167 bp DNA, but the CCAN6E-ΔCT complex failed. The CCANΔCT complex includes CENP-LN, CENP-HIKM and CENP-OPQUR, but not CENP-C and CENP-TWSX; the CCAN6E-ΔCT complex includes charge mutations of positively-charged residues on the CENP-LN (K270E/K296E in CENP-N2E, K155E/R306E/K319E/K321E in CENP-L4E) in contact with DNA; two degradation products of CENP-R annotated as CENP-RΔ1 and CENP-RΔ2 in gray color. Of note, the two separated peaks seen in the elution represent wild type CCAN (red line) and CENP-ANuc–binding deficient CCAN (green line) complex with CENP-ANuc and CENP-ANuc which are indistinguishable. However, DNA binding-deficient CCAN (cyan line) failed to bind nucleosomal DNA, validating that CCAN binds to DNA via CENP-LN. See also Supplementary Figs. S5, S6.