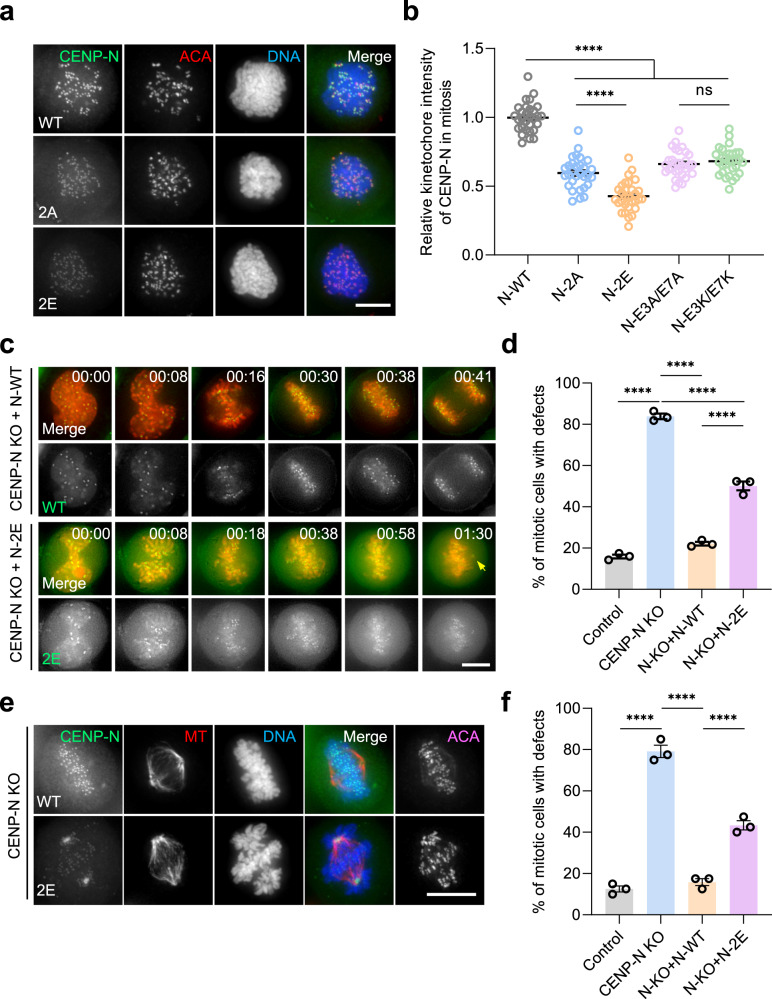
Fig. 3. DNA binding is required for CENP-N centromere localization and function in mitosis.
a Representative immunofluorescence montage of HeLa cells expressing GFP-CENP-N wild type and DNA binding-deficient mutants. Scale bar, 10 µm. Note that K270 and K296 binding to DNA determines CENP-N localization to centromere in mitosis. b Statistical analyses of centromere localization efficacy of CENP-N wild type and mutants. Data present means ± s.e.m. from three independent experiments of 30 cells for each group. Ordinary one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test was used to determine statistical significance. ****p < 0.0001; ns, not significant. c Real-time imaging of HeLa cells with chromosome marked by H2B-mCherry and GFP-tagged CENP-N wild type and 2E mutant in the absence of endogenous CENP-N. Note that 2E mutant caused mitotic arrest with chromosome alignment defect. Scale bar, 10 µm. d Quantification of mitotic phenotypes in cells expressing CENP-N 2E mutant after induction of endogenous CENP-N knockout as in c. Data present means ± s.e.m. from three independent experiments (Control, n = 69; CENP-N KO, n = 68; N-KO + N-WT, n = 68; N-KO + N-2E, n = 68). Ordinary one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test was used to determine statistical significance. ****p < 0.0001. e Representative immunofluorescence montage of HeLa cells expressing GFP-CENP-N wild type and 2E mutant and stained for kinetochore microtubule. Scale bar, 10 µm. Note that 2E mutant failed to localize to centromere which resulted in aberrant spindle and misaligned chromosomes. f Statistical analyses of chromosome alignment efficacy of CENP-N wild type and 2E mutant. Data present means ± s.e.m. from three independent experiments of 120 cells for each group. Ordinary one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test was used to determine statistical significance. ****p < 0.0001. See also Supplementary Fig. S7.