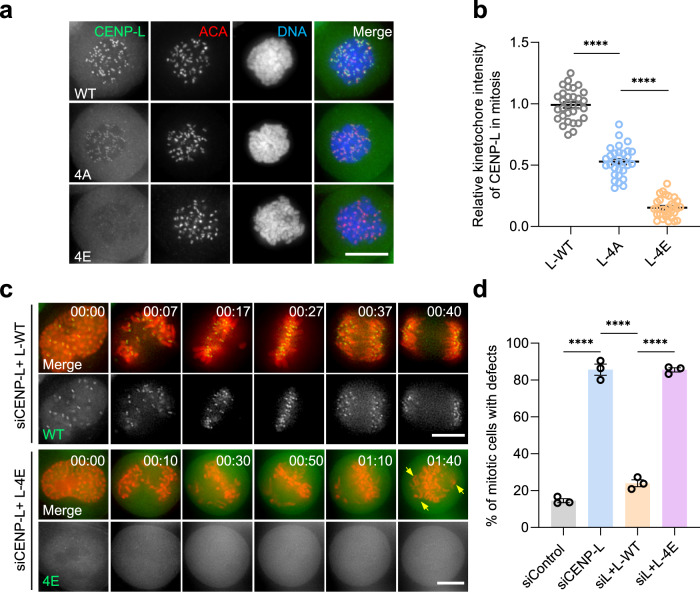
Fig. 4. CENP-L binding to DNA is essential for accurate chromosome segregation.
a Representative immunofluorescence montage of HeLa cells expressing GFP-CENP-L wild type and DNA binding-deficient mutants. Scale bar, 10 µm. Note that K155/R306/K319/K321 determine CENP-L localization to centromere in mitosis. b Statistical analyses of centromere localization efficacy of CENP-L wild type and mutants (4A, 4E). Data present means ± s.e.m. from three independent experiments of 30 cells. Ordinary one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test was used to determine statistical significance. ****p < 0.0001. c Real-time imaging of HeLa cells with chromosome marked by H2B-mCherry and GFP-tagged CENP-L wild type and 4E mutant in the absence of endogenous CENP-L. Note that 4E mutant caused mitotic arrest with chromosome alignment defects. Scale bar, 10 µm. d Quantification of mitotic phenotypes in cells expressing CENP-L 4E mutant after induction of endogenous CENP-L knockout as in c. Data present means ± s.e.m. from three independent experiments of (siControl, n = 67; siCENP-L, n = 68; siL + L-WT, n = 67; siL + L-4E, n = 69). Ordinary one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test was used to determine statistical significance. ****p < 0.0001. See also Supplementary Fig. S8.