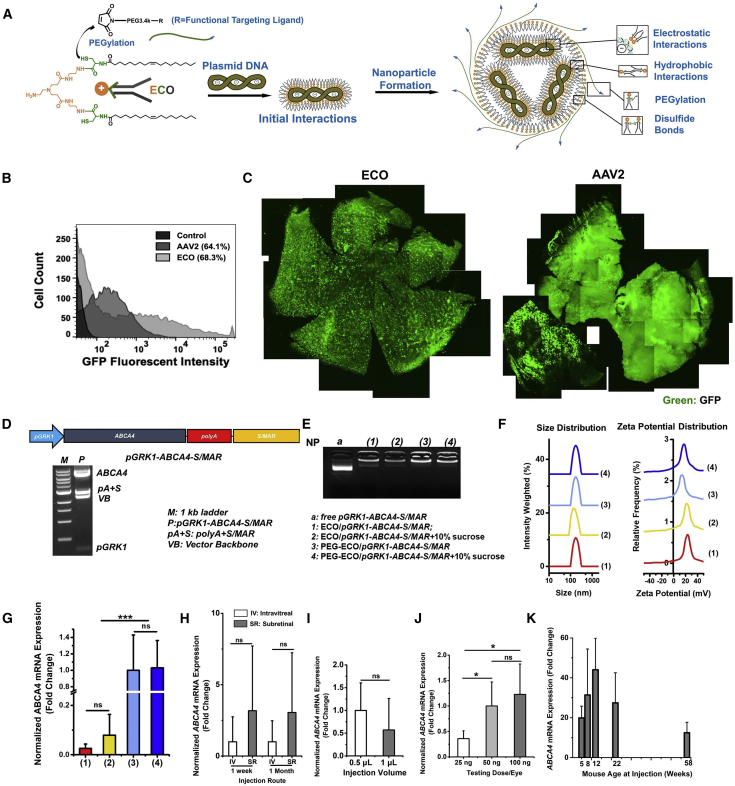
Figure 1.
Formulation and characterization of ECO plasmid DNA nanoparticles
(A) Schematic of self-assembly formulation of ECO/plasmid DNA nanoparticles. (B and C) Flow cytometry histograms of GFP expression in ARPE-19 cells 48 h after transfection with EM-PEG-ECO/pCMV-GFP and AAV2-CMV-GFP (B) and fluorescence images of retinal flat mounts of GFP expression in BALB/c mice 4 months after a subretinal injection of EM-PEG-ECO/pCMV-GFP and AAV2-CMV-GFP (C). (D) Diagram of the therapeutic pGRK1-ABCA4-S/MAR plasmid construct and confirmation of the structure by restriction enzyme digestion agarose gel electrophoresis. (E and F) Characterization of different ECO/pGRK1-ABCA4-S/MAR nanoparticle formulations by agarose gel electrophoresis (E) and DLS of size and zeta potential distribution (F). (G) qRT-PCR of ABCA4 mRNA expression in Abca4−/− mice 1 week after subretinal treatment with (1) ECO/pGRK1-ABCA4-S/MAR, (2) ECO/pGRK1-ABCA4-S/MAR (10% sucrose), (3) PEG-ECO/pGRK1-ABCA4-S/MAR, and (4) PEG-ECO/pGRK1-ABCA4-S/MAR (10% sucrose). The mRNA expressions were normalized to that by PEG-ECO/pGRK1-ABCA4-S/MAR. (H–K) Characterization of in vivo gene expression of PEG-ECO/pGRK1-ABCA4-S/MAR in Abca4−/− mice with different injection routes (intravitreal versus subretinal) (H), injection volume (0.5 or 1 μL, expression normalized to 0.5 μL) (I), injection dose (25, 50, or 100 ng/eye, expression normalized to 50 ng/eye) (J), and age at treatment (K). Analyses were done by qRT-PCR of ABCA4 mRNA expression 1 week or 1 month, as indicated, after single treatment of nanoparticles (100 ng/eye, 0.5 μL). ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.005.