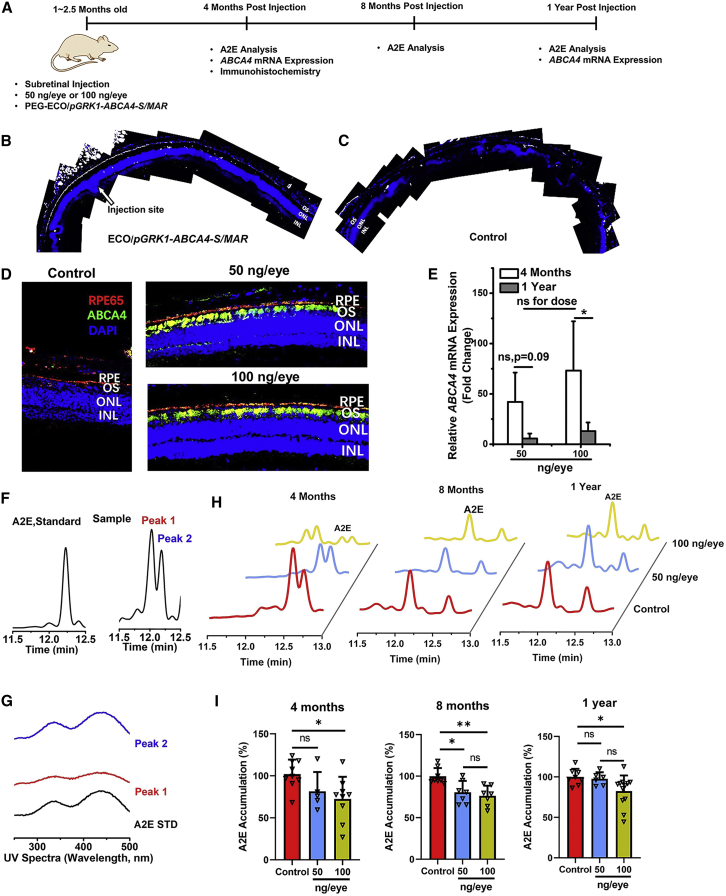
Figure 2.
Treatment efficacy after a single dose of 50 ng or 100 ng/eye with PEG-ECO/pGRK1-ABCA4-S/MAR nanoparticles in Abca4−/− mice
(A) Timeline of treatment with PEG-ECO/pGRK1-ABCA4-S/MAR in Abca4−/− mice. (B and C) ABCA4 expression distribution in the retina of Abca4−/− mice after subretinal treatment with ECO/pGRK1-ABCA4-S/MAR nanoparticles (200 ng/μL, 1 μL) (B) and PBS (C) for 7 days. Analysis was conducted on confocal images of immunohistochemistry (IHC) staining with an ABCA4 antibody (ABCA4 expression is shown in white). (D) Fluorescence IHC staining of ABCA4 in the retina (red, RPE65; green, ABCA4; blue, DAPI) of Abca4−/− mice 4 months after a single treatment of PBS and PEG-ECO/pGRK1-ABCA4-S/MAR (50 ng or 100 ng/eye). (E) qRT-PCR of ABCA4 mRNA expression in Abca4−/− mice 4 months and 1 year after treatment. (F and G) HPLC chromatograms (F) and UV spectra (G) of the A2E standard and A2E from eye samples of 1-year old Abca4−/− mice, where the A2E peak was identified with the same elution time as the A2E standard. (H and I) Representative HPLC chromatograms of A2E (H) and the A2E levels quantified from HPLC relative to the control (I) 4, 8, and 12 months after a single treatment with PEG-ECO/pGRK1-ABCA4-S/MAR (50 ng or100 ng/eye) in Abca4−/− mice (∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01).