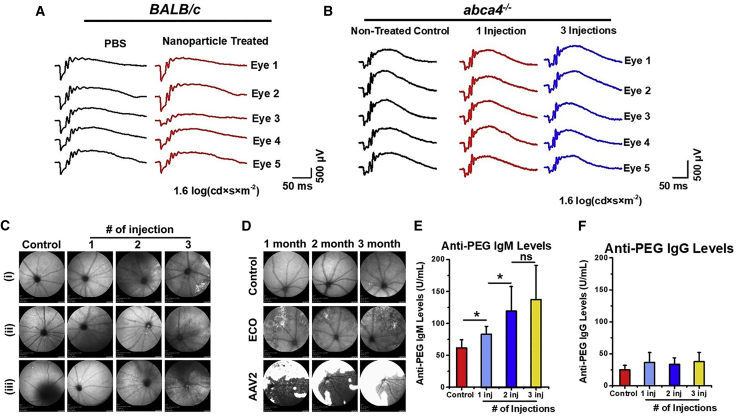
Figure 4.
Safety of subretinal injection of PEG-ECO/DNA nanoparticles
(A and B) Scotopic electroretinogram (ERG) responses of BALB/c mice 1 month after subretinal injection of ECO/pGRK1-ABCA4-S/MAR nanoparticles (A) and of Abca4−/− mice 10–10.5 months after subretinal injection of a single dose (100 ng/eye) or 3 doses (every 3 months, 100 ng/eye) of PEG-ECO/pGRK1-ABCA4-S/MAR nanoparticles (B) at a test light intensity of 1.6 log(cd × s × m−2). (C) Eye morphology, demonstrated by scanning laser ophthalmoscopy (SLO), of Abca4−/− mice that received multiple treatments of PEG-ECO/pGRK1-ABCA4-S/MAR nanoparticles 7 months after the initial treatment (control, untreated). (D) Eye morphology (SLO) of BALB/c mice treated with EM-PEG-HZ-ECO/pCMV-GFP nanoparticles and AAV2-CMV-GFP (dose, 5 × 109 gene copies; control, untreated) 1, 2, and 3 months after treatment (large white area, potential inflammation). (E and F) PEG antibody analysis of anti-PEG IgM (E) and anti-PEG IgG (F) levels from the blood of Abca4−/− mice that received multiple treatments of PEG-ECO/pGRK1-ABCA4-S/MAR nanoparticles. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.005, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001.