Figure 2. Epigenetic regulation of autosomal and X chromosome-specific imprinting.
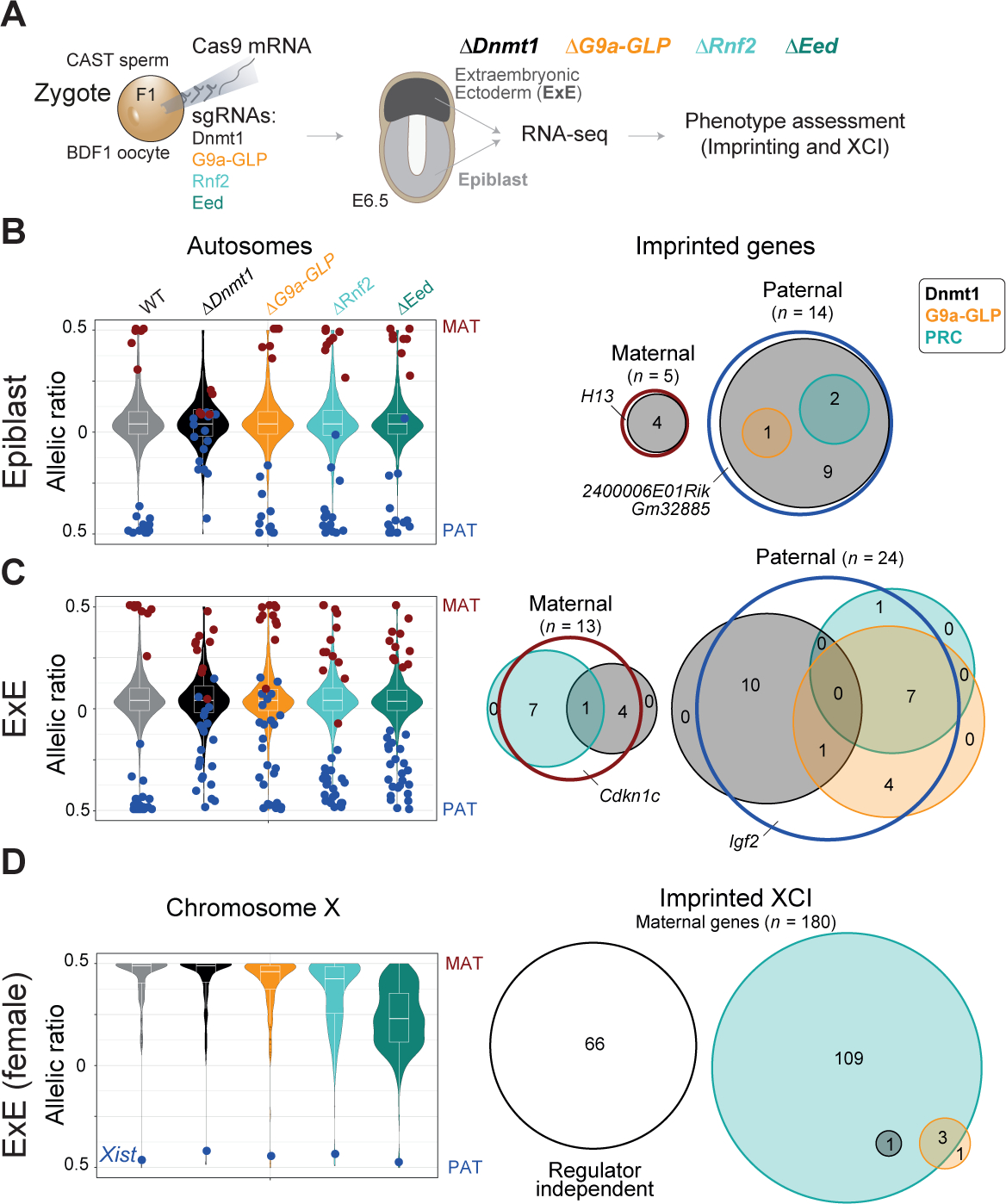
(A) Schematic overview for our strategy to assign roles for selected epigenetic regulators to parent-specific gene expression. Target epigenetic regulators are disrupted by injection of Cas9 and sgRNAs into hybrid F1 (BDF1xCAST) zygotes (ΔDnmt1 n = 3, ΔG9a-GLP n = 9, ΔRnf2 n = 8, ΔEed n = 10). E6.5 Epiblast (light grey) and extraembryonic ectoderm (ExE, dark grey) were collected from each selected embryo. Regulator colors are used throughout the rest of the manuscript: Dnmt1, black; G9a and GLP, orange, gene name Ehmt1 and Ehmt2; PRC1 member Rnf2, light turquoise; and PRC2 member Eed, turquoise.
(B) Left: Violin plots of the median allelic ratios of autosomal genes from WT and regulator mutants in Epiblast. Maternal and paternal expressed imprinted genes are indicated with red and blue dots, respectively. Right: Venn diagram shows the intersection of each epigenetic regulators’ contribution to imprint status. An epigenetic regulator was counted as relevant for silencing imprinted genes if the change in allelic ratio between WT and KO was ≥ 20%. PRC1 and PRC2 were summarized as PRC by using the higher delta. In Epiblast, DNA methylation-dependent imprinting is most frequent. Regulator independent imprinted genes have a delta allelic ratio < 20% in all disrupted regulators (see Figure S3B). Imprinted genes with less than two informative allelic ratio values in any regulator disruption data set are not shown.
(C) As in (B) for ExE. Extraembryonic imprints appear to depend on a more diverse set of regulators.
(D) Left: Violin plots displaying the median allelic ratio of X-linked genes from WT and regulator mutants in female ExE. The blue dot highlights the allelic ratio of the lncRNA Xist. Successful extraembryonic XCI depends on PRC2 and, to a lesser degree, PRC1. Notably, paternal Xist expression is largely stable in all regulator mutants examined (Figure S2H). Right: Venn diagram for imprinted XCI as shown for autosomal imprinting in (B) and (C). An epigenetic regulator was counted as relevant for silencing X-linked genes if the delta allelic ratio change between WT and KO for any regulator was ≥ 20%. Regulator independent X-linked genes have a delta allelic ratio < 20% in all disrupted regulators.
