Figure 5.
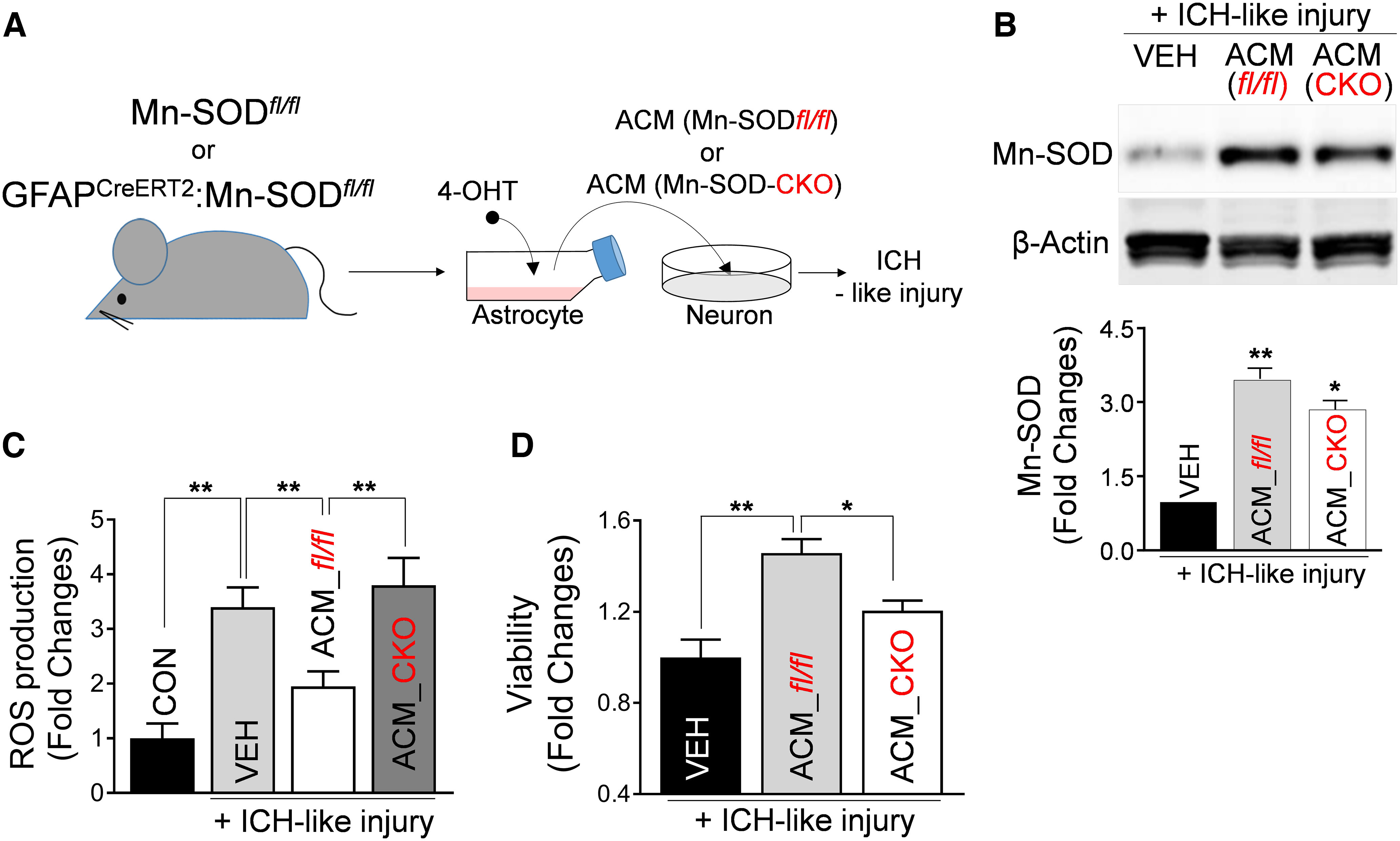
Mn-SOD-deficient astrocytic Mt fails to inhibit ROS overproduction and protects neurons against ICH-like injury. A, Schematic diagram of Mt transfer from Mn-SOD-deficient astrocytes to neurons in vitro. Astrocytes in culture generated from Mn-SODfl/fl mice or Mn-SODfl/fl: hGFAPCreERT2 mice were treated with 1 μm 4-OHT for 48 h to promote recombination. Knockdown of Mn-SOD in the cultured astrocytes from Mn-SODfl/fl: hGFAPCreERT2 mice was confirmed by Western blot analysis, as well as qRT-PCR (Extended Data Fig. 5-1). After washing the cells, fresh medium was supplied to astrocyte cultures. Twenty-four hours later, ACM from cultured astrocytes from Mn-SODfl/fl mice (ACM_Mn-SODfl/fl) or Mn-SODfl/fl: hGFAPCreERT2 mice (ACM_Mn-SOD-CKO) were collected and transferred onto cultured neurons. After a 24 h incubation with ACM from Mn-SODfl/fl or Mn-SOD-CKO astrocytes, the neurons were exposed to ICH-like injury for 48 h (for cell viability) or 12 h (for ROS generation). B, Representative Western blot image and illustrating graph showing Mn-SOD protein levels in cultured neurons that were pretreated with control culture media (VEH), ACM_Mn-SODfl/fl or ACM_Mn-SOD-CKO for 24 h, followed by exposure to ICH-like injury for 48 h. VEH, Vehicle. The significant changes in Mn-SOD/β-actin levels were assessed by one-way ANOVA/Fisher's LSD test (n = 6 per group), **p < 0.01 (p < 0.0001, VEH plus ICH-like injury vs ACM_Mn-SODfl/fl plus ICH-like injury), t value (t = 10.99); *p < 0.05 (p = 0.0173, ACM_Mn-SODfl/fl plus ICH-like injury vs ACM_Mn-SOD-CKO plus ICH-like injury), t value (t = 2.676). C, ROS generation in rat cortical neurons pretreated with ACM from Mn-SODfl/fl or Mn-SOD-CKO astrocytes for 24 h, followed by ICH-like injury for 12 h. The significant changes in ROS generation were assessed by one-way ANOVA/Fisher's LSD test (n = 13 per group), **p < 0.01 (p < 0.0001, CON vs ICH-like injury), t value (t = 4.668); **p < 0.01 (p = 0.0070, VEH plus ICH-like injury vs ACM_Mn-SODfl/fl plus ICH-like injury), t value (t = 2.82); **p < 0.01 (p = 0.0008, ACM_Mn-SODfl/fl plus ICH-like injury vs ACM_Mn-SOD-CKO plus ICH-like injury), t value (t = 3.598). CON. Control. D, Viability of rat cortical neurons treated with ACM_Mn-SODfl/fl or ACM_Mn-SOD-CKO for 24 h, followed by ICH-like injury for 48 h. Viabilities were measured by LDH assay. Values represent fold change of viabilities compared with VEH plus ICH-like injury group. The significance in cell viability was assessed by one-way ANOVA/Fisher's LSD test (n = 6 per group), **p < 0.01 (p = 0.0001, VEH plus ICH-like injury vs ACM_Mn-SODfl/fl plus ICH-like injury), t value (t = 5.159); *p < 0.05 (p = 0.0121, ACM_Mn-SODfl/fl plus ICH-like injury vs ACM_Mn-SOD-CKO plus ICH-like injury), t value (t = 2.854). Data are shown as mean ± SEM. ACM_fl/fl, ACM_Mn-SODfl/fl.
