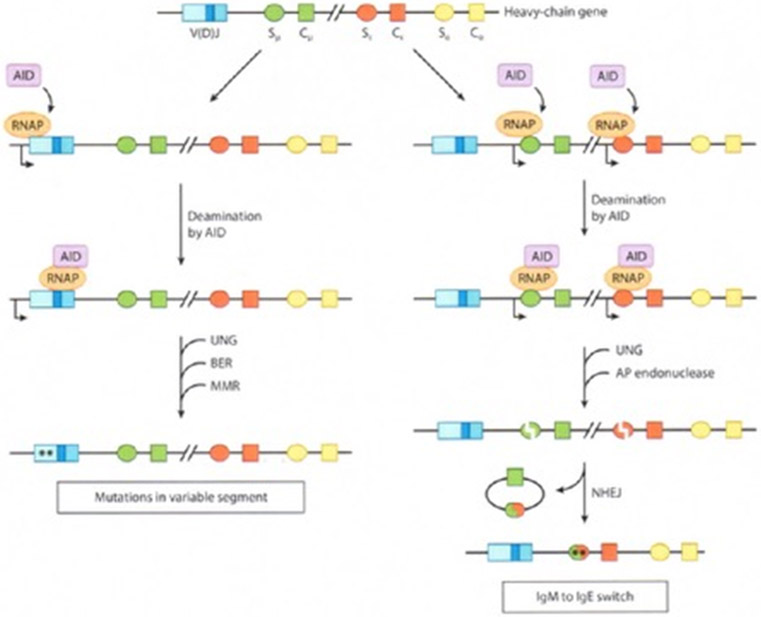
Figure 5.
A model for somatic hypermutation (SHM) and class-switch recombination (CSR) during antibody maturation. Different sequence elements are shown as rectangles or ovals of different colors. The direction of transcription is indicated by a rightward arrow. AID is recruited at a proximal pause site for RNAP II. Following release from the pause, AID travels with RNAP II as it transcribes DNA and converts cytosine to uracil on each DNA strand. Uracil is excised by uracil N-glycosylase (UNG) and processed by error-prone base-excision repair (BER) or by mismatch repair (MMR) to introduce point mutations, which are indicated by asterisks. To initiate CSR, double-strand breaks are generated by AP endonuclease (64a) incision at UNG-generated apurinic/apyrimidinic AP sites. Broken ends are ligated by the nonhomologous end-joining (NHEJ) pathway, and the intervening DNA is released as a switch circle. Abbreviations: C, constant segment (only the μ, ε, α regions are shown); S, switch region preceding each C segment; V(D)J, variable segment.