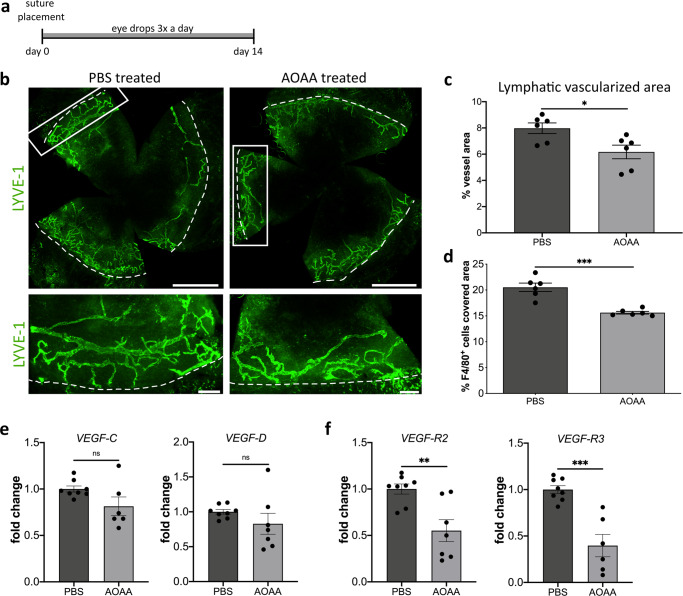
Fig. 7. CBS-inhibition by AOAA treatment reduces inflammation-induced lymphangiogenesis in C57BL/6 N mice.
a Schematic description of the suture‐induced model of corneal neovascularization: Intrastromal sutures were placed into the cornea of the animals (day 0). Mice were then treated with AOAA (4 mM) or PBS eyedrops 3 times a day for 2 weeks until end of experiment (day 14). b Representative corneal whole mounts of inflammation-induced lymphangiogenesis of C57BL/6 N stained for LYVE-1. The boxed areas in the top panels are shown in higher magnification in the bottom panels. Dashed lines show the border between the limbus and the cornea. Scale bars: 1 mm (top panel) 200 µm (lower panel). c Quantification of the inflammatory lymphatic vascularized area of the whole mounts. Data are expressed as means ± SEM (n = 6). d Quantification of area covered with F4/80+ macrophages in the inflamed cornea. Data are expressed as means ± SEM (n = 6). Determination of mRNA levels of (e) VEGF-C, and VEGF-D and (f) VEGF-R2, and VEGF-R3 in corneas of mice treated with AOAA (4 mM) (n = 7) or PBS eyedrops for 14 days (n = 8). Data are presented as means ± SEM. Statistical significance was calculated by two-tailed t-test *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001.