Fig.6. The key role of mitochondria in kidney disease development.
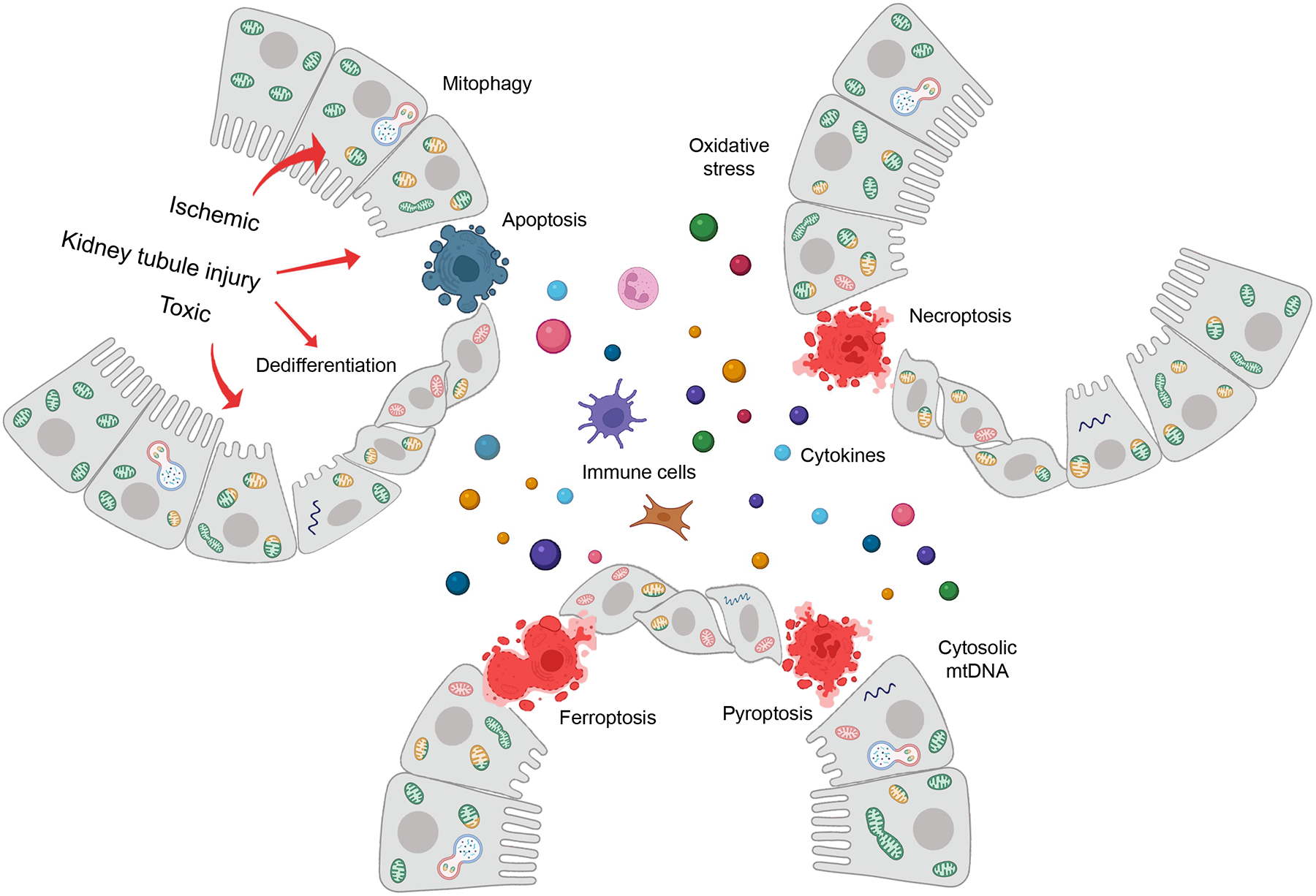
The figure illustrates the overall biological changes in response to mitochondria damage in kidney tubules following toxic or ischemic injury. Mitochondrial injury in kidney tubule cells will lead to energy deficiency, increase reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation, the cytosolic release of mitochondrial DNA. Mitochondria biogenesis, change in shape, size, and turn-over play role in kidney tubule function. Severe injury will lead to cell death including apoptosis, necroptosis, pyroptosis, ferroptosis, and enhance inflammation and fibrosis by releasing pro-inflammatory cytokines, attracting immune cells, or activating fibroblasts.
