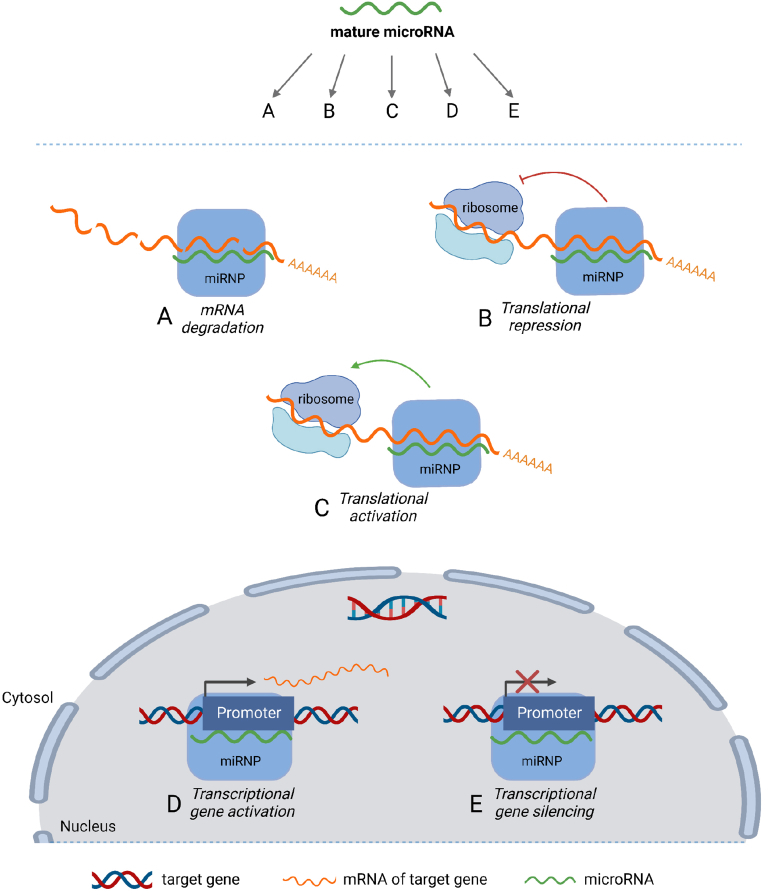
Figure 1.
Mechanisms of miRNA-mediated gene expression regulation. A mature ∼22 base pair miRNA is loaded into the microRNA ribonucleotide complex (miRNP) after enzymatic processing in one of the miRNA maturation pathways. This miRNA may then, via the miRNP, affect gene expression through several different mechanisms depending on the miRNA-mRNA pair in question and the cellular context. Binding of the miRNP to target mRNA sequences can lead to mRNA degradation (A) or repression of mRNA translation into protein (B) – the two canonical mechanisms of miRNA action. Binding of some miRNA species to certain targets have been shown to increase translation (C) rather than repress it. Furthermore, some miRNA species have been shown to bind to gene promoter sequences in the nucleus, acting as either activators (D) or silencers (E) of transcription.