Figure 1.
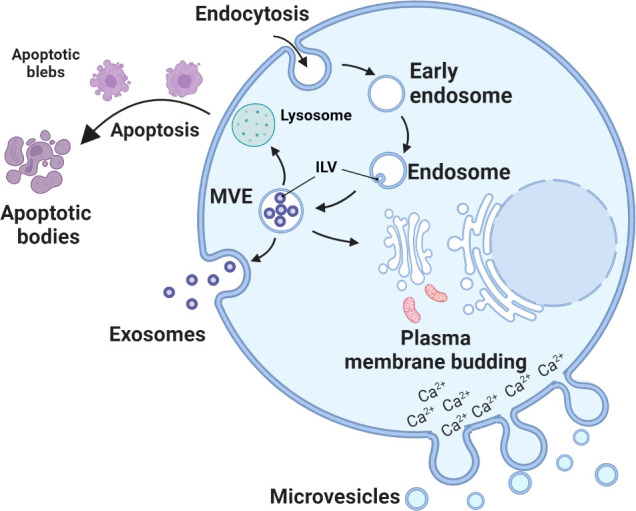
Biogenesis of urinary extracellular vesicles (uEVs). Exosome biogenesis starts from inward budding of the plasma membrane (endocytosis) and eventual formation of early endosomes. The membranes of early endosomes invaginate and bud into surrounding luminal space with cytoplasmic content to form intraluminal vesicles (ILVs) (29). Late endosomal structures containing ILVs are known as multivesicular endosomes (MVEs), which are eventually transported to the trans-Golgi network for endosome recycling, delivered to lysosomes for degradation of all carried material, or fuse with the plasma membrane and release exosomes outside the cell (30). Microvesicles arises through outward budding and fission of plasma membrane and is the result of dynamic interplay between phospholipid redistribution and cytoskeletal protein contraction (31, 32). Apoptotic bodies are formed during apoptosis. Apoptosis progresses through several stages, first nuclear chromatin condensation, then nuclear splitting and the frequent appearance of micronuclei, then membrane blebbing and finally splitting of the cellular content into distinct membrane-enclosed vesicles, termed apoptotic bodies (33, 34).
