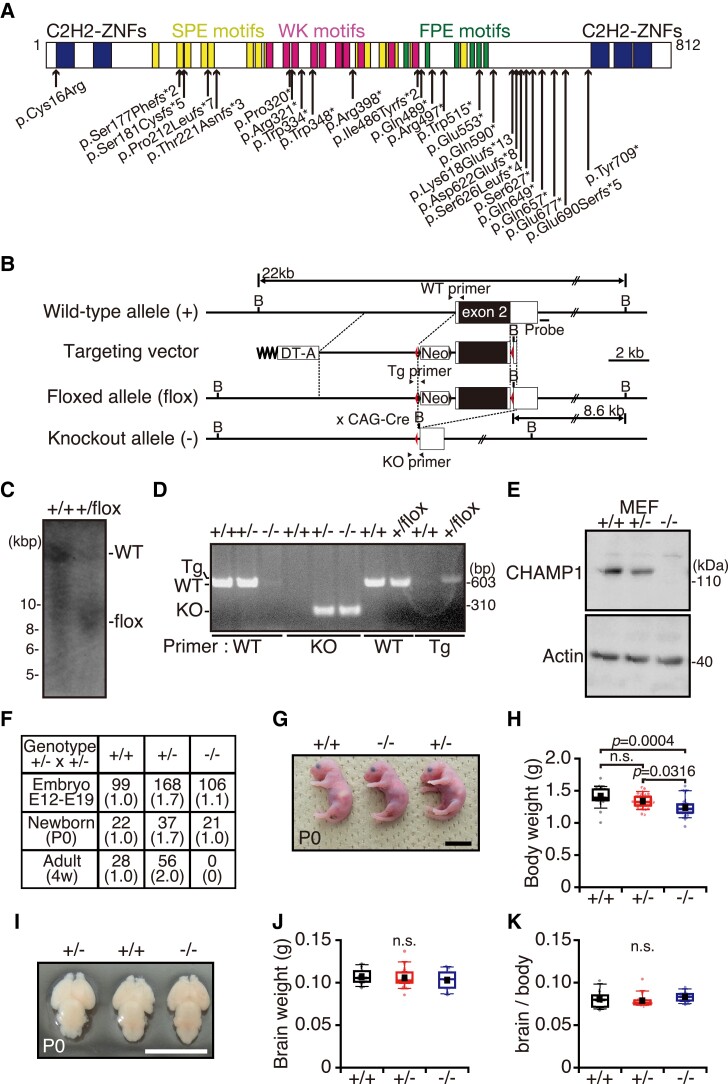
Figure 1.
CHAMP1 −/− mice show a newborn lethal defect. (A) CHAMP1 mutations found in individuals with ID. A schematic structure of CHAMP1 and its ID-associated de novo mutations are shown. fs, frameshift; *, premature stop codon. (B) A schematic of construction of the CHAMP1-knockout allele. Positions of the probes for Southern blotting and PCR primers are indicated. Red triangle shows positions of the lox-P sites. Neo, neomycin-resistance gene; DT-A, diphtheria toxin A gene; B, BamHI site. (C) Southern blot analysis of genomic DNA prepared from CHAMP1+/+ and CHAMP1+/flox mice with the probe shown in (B). (D) Genotyping PCR analysis of CHAMP1+/+, CHAMP1+/flox, CHAMP1+/−, and CHAMP1−/− mice using the primer sets shown in (B). (E) IB analysis of lysates prepared from MEFs isolated from CHAMP1+/+, CHAMP1+/−, and CHAMP1−/− mice using antibodies as indicated. (F) Number and ratio of CHAMP1+/+, CHAMP1+/−, and CHAMP1−/− mice from crosses of C57BL/6J CHAMP1+/− mice. (G) Representative picture of newborn CHAMP1+/+ (left), CHAMP1+/− (right), and CHAMP1−/− (middle) mice. Scale bar: 1 cm. (H) Comparison of the body weight of newborn mice (CHAMP1+/+; n = 19, CHAMP1+/−; n = 36, CHAMP1−/−; n = 19). (I) Representative pictures of newborn CHAMP1+/+ (middle), CHAMP1+/− (left), and CHAMP1−/− (right) mouse brains. Scale bar: 1 cm. (J, K) Absolute brain weight (J) and ratios of brain weight to body weight (K) of newborn mice (CHAMP1+/+; n = 8, CHAMP1+/−; n = 14, CHAMP1−/−; n = 8). For box plots in (H, J, K), the bottom and top of the box show the lower and upper quartile values, respectively. The mean is indicated with a filled square and the median is indicated with a bar in the box. The bottom and top of the whiskers denote the 10th and 90th percentiles, respectively. P values were determined by Tukey–Kramer test. n.s., not statistically significant.