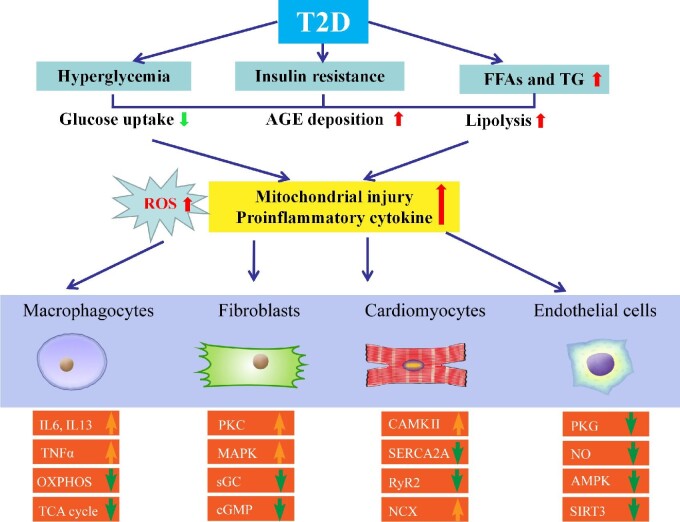
Figure 2.
Molecular mechanisms behind HFpEF with T2D. Various metabolic abnormalities in T2D play an essential role in conjunction with the buildup of proinflammatory cytokines and ROS. Other confounding factors, including hyperglycemia, lipotoxicity, and increased levels of FFA, insulin, and AGEs, also contribute to HFpEF. Compromised NO bioavailability and sensitivity, oxidative stress and inflammation, and impaired angiogenesis are involved. Crucial molecular contributors to pathological hypertrophy include G protein-coupled receptors, stress hormone ligands, and signaling kinases in T2D with HFpEF. Relaxation period includes active and passive phases. Downregulated insulin signaling is a hallmark of T2D along with changes in other signaling cascades, including downregulated AMPK signaling and hyperactivated PKC and MAPK. IL6, interleukin 6; IL13, interleukin 13; OXPHOS, oxidative phosphorylation; TCA, tricarboxylic acid cycle; TNFα, tumor necrosis factor-α.