Fig. 3.
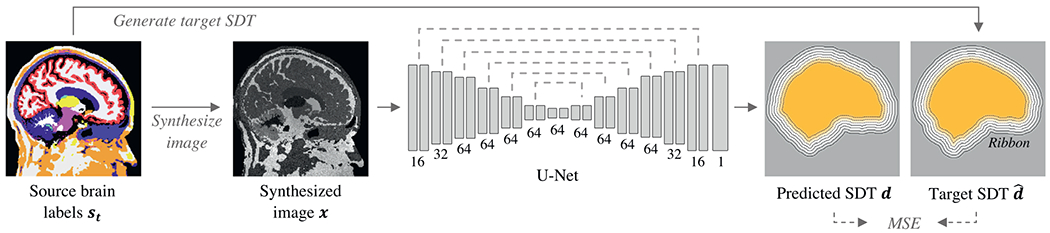
SynthStrip training framework. At every optimization step, we sample a randomly transformed brain segmentation st, from which we synthesize a gray-scale image x with arbitrary contrast. The skull-stripping 3D U-Net receives x as input and predicts a thresholded signed distance transform (SDT) d representing the distance of each voxel to the skull boundary. The U-Net consists of skip-connected, multi-resolution convolutional layers illustrated by gray bars, with their number of output filters indicated below. We train SynthStrip in a supervised fashion, maximizing the similarity between d and the ground-truth SDT within a ribbon of set distance around the brain and derived directly from the segmentation labels of st.
