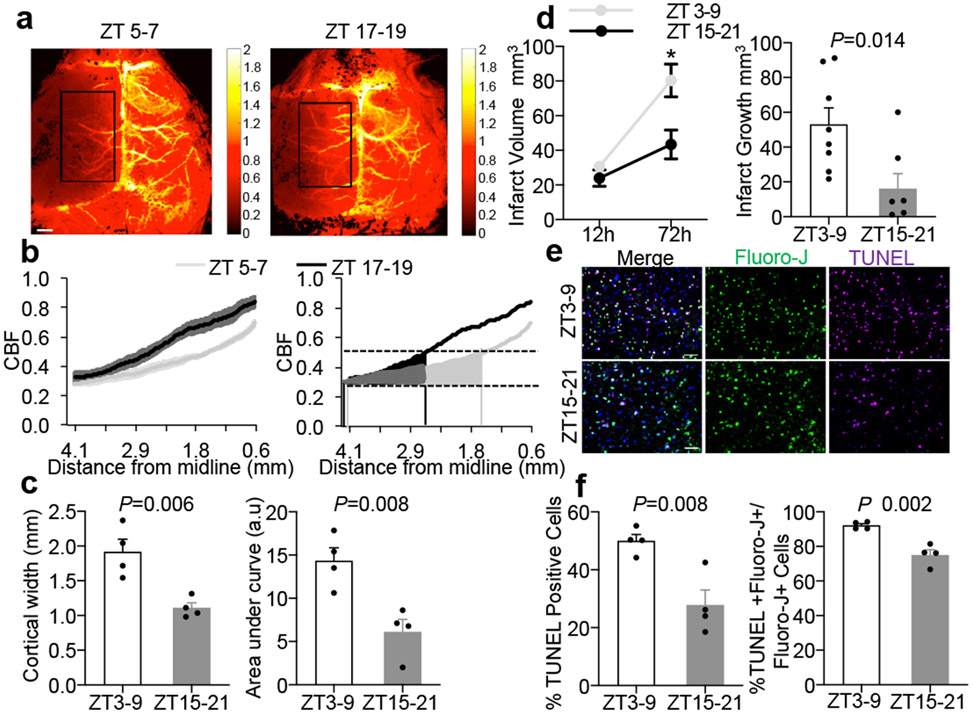
Figure 2. Comparisons of penumbra after focal cerebral ischemia.
a. Laser speckle imaging at 25 mins post-MCAO in ZT5-7 versus ZT17-19 C57BL6 mice. Rectangular area for quantifying data from 4 independent experiments/mice per group in (b) and (c). Scale: 1 mm. b. Ipsilateral blood flow gradients were steeper in ZT17-19 versus ZT5-7 images (line is mean, shaded areas are SEM, left panel; area-under-curve, right panel). c. The blood flow penumbra was operationally defined as average cortical width or area-under-curve between 30-50% of normal levels, based on a lower threshold of infarction and an upper threshold of gene expression and protein synthesis inhibition (25-55 mL/100g/min, see Methods and References15,16). The penumbra was narrower in ZT17-19 versus ZT5-7 mice. Physiologic parameters were similar across all animals (Extended Data 5). Penumbral perfusion was not correlated with blood pressure or pCO2 (r2 = 0.006 and 0.171 respectively). d. Infarct growth (12 to 72 hrs) after 60 min MCAO was smaller in ZT15-21 (n=8) versus ZT3-9 (n=9) mice. e. Representative TUNEL, fluoro-jade and DAPI immunostaining in penumbral cortex at 24 hrs after 60 min MCAO in mice. Scale: 50 μm. f. Percentages of TUNEL/DAPI and TUNEL plus fluoro-jade/fluoro-jade were lower in ZT15-21 versus ZT3-9 penumbra (n=4 mice per group). All values in Figure 2 are mean ± SEM; comparisons via 2-tailed t-test.