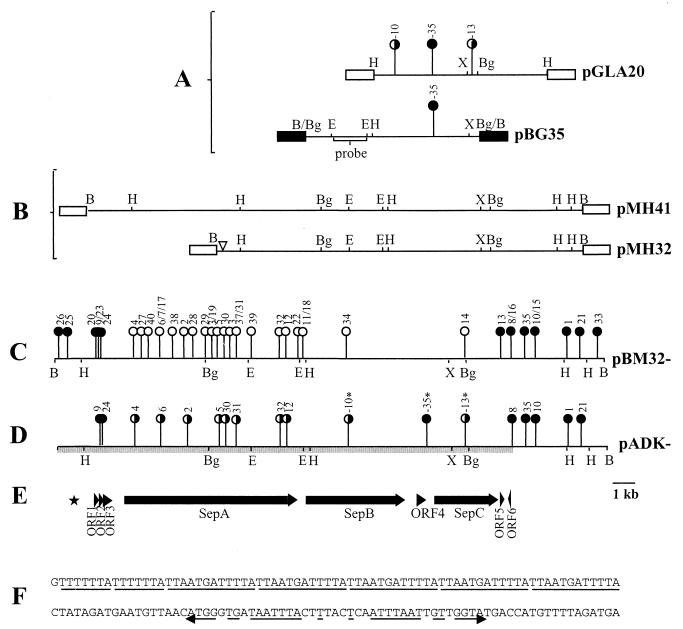
FIG. 1.
(A) The HindIII fragment from pADAP cloned into pLAFR3 to form pGLA20, showing locations of the mini-Tn10 103 insertion mutations at positions -10, -13, and -35 (18). Results of bioassay of mutants against the grass grub are shown. The map of pBG35 shows the relative position of pGLA20-35 mutation and the location of the 2.2-kb EcoRI fragment used as a probe to screen the pADAP BamHI library. (B) Restriction enzyme maps of the pathogenic clones pMH32 and pMH41. (C) Locations and phenotypes of mini-Tn10 insertions in pBM32. (D) Bioassay results of the pADK recombinants. (E) Schematic diagram of the sequenced region. (F) Nucleotide sequence of the 7-bp repeat, five-copy 12-bp repeat, and the downstream degenerate 34-bp inverted repeat. ∗, pADK mutations isolated by Grkovic et al. (20); filled circles, mutations that resulted in an unaltered pathogenic phenotype (clear gut, nonfeeding); open circles, mutations that resulted in the abolition of pathogenicity; half-filled circles, mutations that induced a nonfeeding pathotype without clearance of the gut; ▿, site of internal deletion; ■, pBR322 vector DNA; □, pLAFR3; ★, location of nucleotide repeats. Arrows indicate ORFs and their orientation. Abbreviations for restriction enzymes: B, BamHI; Bg, BglII; E, EcoRI; H, HindIII; X, XbaI.